Clipart tagged: ‘maxillary’
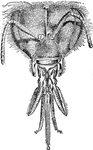
Honey Bee
"Head and Appendages of Honey-bee (Apis). a, Antenna or feeler. g, Epipharynx. mxp, Maxillary palp.…
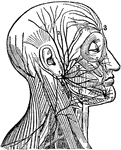
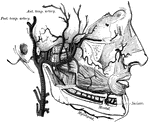
Facial Nerve
"(1) The facial nerve at its emergence from stylo-mastoid foramen; (2) temporal branches communicating…
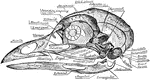
Skull of a Common Fowl
"Fig. 62 Skull of common fowl, enlarged. from nature by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A. The names of bones…
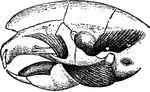
Hystrix Eristata
"Skull of Hystrix Eristata. t, temporal muscle; m, masseter. m', portion of masseter transmitted through…
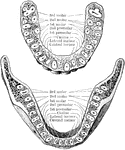
Jaw Showing Roots of Teeth
Horizontal section through both the upper and lower jaws to show the roots of the teeth. The sections…
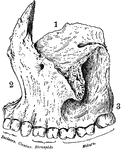
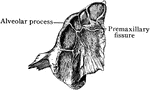
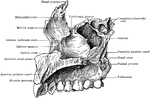
Human Maxillary (Upper Jaw) Bone
Superior maxillary bone. With it's fellow on the opposite side, it forms the whole of the upper jaw.…
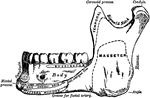
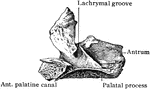
Human Maxillary (Upper Jaw) Bone
Inferior Maxillary Bone (lower jaw). It is the largest and strongest bone in the face and serves for…
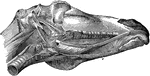
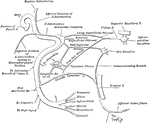
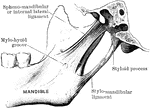
Muscles of the Maxillary Space of a Horse
Right infero-lateral view of the muscles of the maxillary space, the ramus and hyoid cornu are cut away.…
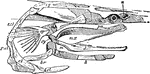
Polyodon
"Skull of Polyodon. n, nasal cavity; sq, squamosal; mh, hyomandibular; sy, symplectic; pa, palate-pterygold;…

Polypterus Skull
"Upper aspect of the primordial cranium, with the membrane-bones removed. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…
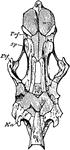
Polypterus Skull
"Lower aspect of the primordial cranium, with the membrane-bones removed. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…
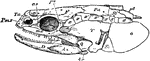
Polypterus Skull
"Side view, with the membrane-bones. An, angular; ao, anteorbital; Ar, articulary; B, basal; D, dentary;…
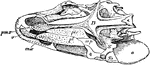
Polypterus Skull
"Lower aspect of the skull, part of the bones being removed on the side. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…
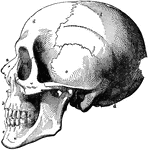
Human Skull
The skull. Labels: a, nasal bone; b, superior maxillary; c, inferior maxillary; d, occipital; e, temporal;…
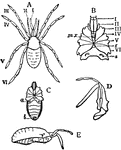
Stylocellus Sumatranus
"Stylocellus sumatranus, one of the Opiliones; after Thorell. Enlarged. A, Dorsal view; I to VI, the…
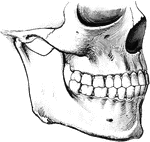
Teeth
To show the relation of the upper to the lower teeth when the mouth is closed. The manner in which a…