Clipart tagged: ‘strata’
Basin of Middle Tennessee
Different physiografic provinces make up the Basin of Middle Tennessee. Sections from east to west across…
Coastal Plain After Elevation
A coastal plain after elevation and renewed dissection. Two cuestas and two lowlands are now produced…
Compound Regressive-Transgressive Series
Diagram showing the relationship of the strata in five successive sections, in a compound regressive-transgressive…

Cuestas and Lowlands
Block diagram illustrating the formation of three cuestas and lowlands by normal drainage on the peneplaned…
Eozoic Strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural: strata) is a layer of rock or soil with internally…
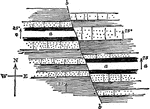
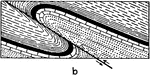
Strike Fault
"The two faults of larger throw, by which a single sheet of trap is represented in three ridges, are…
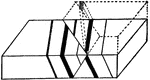
Thrust Fault Diagram
Diagram illustrating the offset of strata produced by vertical slipping along an inclined plane, when…
Gravel Hill
"Suppose a to be a gravel hill, and b a strata of clay or rock, impervious to water. The fluid percolating…

Hog-back Diagram
Hog-backs (RR) changing into cuestas (CC) and these into steps (HH) by progressive flattening of strata;…
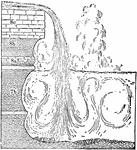
Horseshoe Falls, Niagara
Section of the Horseshoe Falls, Niagara, to show the depth of water below the falls and the arrangement…

Iguanodon
An extinct fossil colossal lizard found in the Wealden strata; so called from the resemblance of its…

Laccolith
"Conduit of Tilford laccolith, showing porphyry (P) breaking across limestone (L)." -Walcott, 1901
Niagara Falls
This illustration represents a section of the rocks along the river below Niagara Falls. It gives some…
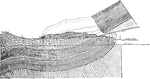
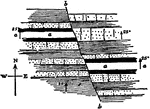
North Hill Overthrust
Section through North Hill, Kingston, N.Y. showing the overthrust which led to a repetition of the strata.
Michigan Peninsula
Strata (plural of stratum), is the geological formation of an area of land. A sequence of discrete rock…

Pulpit Rock Sections
Parallel vertical or columnar sections on the face of Pulpit Rock, near Colorado Springs, through identical…
Rock Layers Showing Geological Periods
"Diagrammatic structure section of the Wasatch Range in Ogden Canyon." -Lee, 1915

Rock Layers Showing Types of Rock
"Cross section of Marsh Creek valley at McCammon, Idaho." -Lee, 1915

Sandy Stratum
"A sandy stratum, a a, acting as a filter, occupies an inclined position between two other strata impervious…
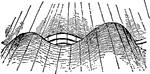
Diagram of Undulating Strata Cut by a Fault
An illustration of undulating strata cut by a fault with alternate throw in opposite directions.
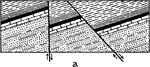
Strata Transversed by a Diminshing Strike Fault
An illustration of a plan of strata transversed by a diminishing strike fault.

Strata with Fault Line
An illustration of strata bent at a line of fault. In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural:…
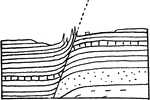
Uncomformable strata
"In some places a series of strata A, having a certain dip, rest directly upon the eroded surface of…
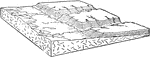
Overdeepened Subsequent Stream
Subsequent streams are streams whose course has been determined by selective headward erosion along…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…
Synclinal Region
This illustration represents the effects of erosion of a synclinal region consisting of alternations…