Tides
The Tides ClipArt gallery contains 14 illustrations showing the cause of tides from an astronomical perspective as well as diagrams of tide contours.
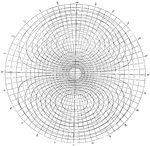
Cotidal Lines
This figure "shows the cotidal lines and the lines of equal rise and fall for a diurnal component in…
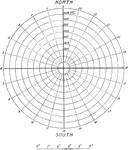
Diurnal Cotidal Lines
This figure shows "the cotidal lines and lines of equal amplitude for a diurnal tide in a circular sea…
Diurnal Cotidal Lines
This figure shows "the cotidal lines and lines of equal amplitude for a diurnal tide in a circular sea…
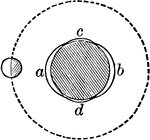
Lunar Tide
If the earth were uniformly covered with a layer of water, the passage of the moon over any place as…
Neap Tides
"The elevation of the tides at c and d is produced by the causes already explained; but their elevation…

Positions
The flood tides are the highest, and the ebb tides are the lowest. These are called spring tides.…
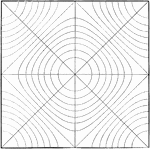
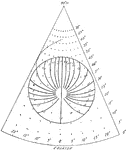
Tide Theory, Square
The figure shows the harmony and syzygy of tides in four different places (the four corners of the square).
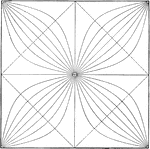
Tide Theory, Square
The figure shows the harmony and syzygy of tides in four different places (the four corners of the square).
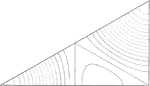
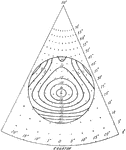
Tide Theory, Triangle
The figure shows a 30 degree triangle made from a square depicting the harmony and syzygy of tides in…

Tide Theory, Triangle
The figure shows a 30 degree triangle made from a square depicting the harmony and syzygy of tides in…
Tides
"Let m be the Moon, and E the Earth covered with water. As the Moon passes round the Earth, its solid…
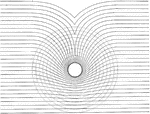
Island Tides
The figure "shows the effect of a circular island upon the cotidal lines." -Coast and Geodetic Survey,…