This science ClipArt gallery offers 102 images of methods to produce power by steam, including the coal-powered steam engine often seen on early trains and steamboats.
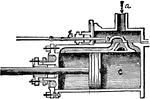
Steam Engine
A machine for utilizing the elastic force of steam as a motive power, and now constructed in a variety…
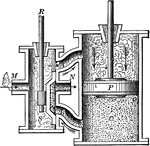
Steam Engine
"The steam engine is a powerful device for utilizing the energy involved in the elasticity and expansive…
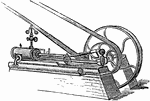
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. Steam…

Steam Engine
"An engine designed to throw a continuous stream of water through a hose upon a conflagration, for the…
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve is Closed
"The relative positions of crank, eccentric and valve when the exhaust closes on the crank end and compression…
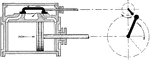
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Where Steam is Admitted to the Slide Valve
"While the crank is moving from the position, steam is being admitted to the head end and being exhausted…
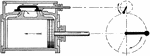
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve is in Open Position
An illustration of the valve with lap at the end of the crank end steam compression. The piston will…
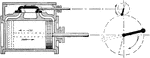
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve Moved to Open Position
"If the inside lap is increased, the valve must move farther before released occurs and the crank angle…
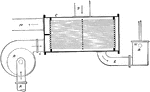
Steam Engine Condenser with Pumps
An illustration of the water entering and exiting the condenser through pump. The cooling water enters…
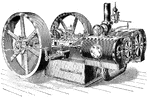
Cross Compound Steam Engine
Illustration of a cross compound steam engine. The engine is designed to hold pressure until the engine's…
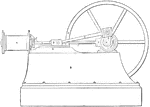
Low Power Simple Steam Engine Diagram
A low power steam engine. The piston inside cylinder A moves the wheel, generating power at 100 horsepower…
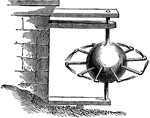
Hero's Steam Engine
"High volumes of steam were pumped into the hollow sphere. The steam would then escape through the many…

Low Power Simple Expansion Steam Engine
A low power simple expansion steam engine. The steam engine can run at 100 horsepower, and not run continuously.…
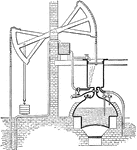
Newcomen Atmospheric Steam Engine
An illustration of Newcomen atmospheric steam engine. The boiler heats the water to build up steam in…
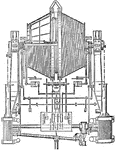
Plan of Direct Acting Hoisting Machine with Corliss Steam Engines for Mining
A plan of direct acting hoisting machine for mining industry. The machine is operated by compound Corliss…
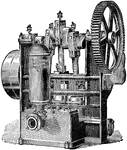
Power Pump Steam Engine
A power pump steam engine without shaft. The engine turns the wheel with the reciprocal motion of the…
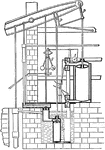
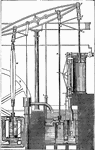
Watt's Final Steam Engine Design
The illustration showing Watt's final steam engine design. The engine is fitted with series of rods…
Steam engines
"The steam engine, in its many forms, is the agent by means of which part of th eenrgy stored up in…
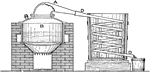
A Still Showing the Separation of a Liquid from a Solid
"Figure 5 shows a form of the apparatus for separating a liquid from another of different boiling point,…
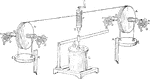
Thermodynamics Apparatus Showing the Relationship between the First and Second Principals
"The falling weights EE turned a paddle-wheel stirrer inside the cylindrical vessel G, which was filled…
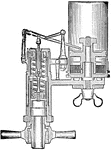
Thompson Indicator for Steam Engine
"The indicator consists of a cylinder in which a piston is fitted, a spring, multiplying lever, and…
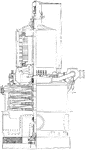
9000 Kilowatts Vertical Curtis Turbine
An illustration of 9000 kilowatts capacity vertical Curtis turbine. Each turbines are located between…
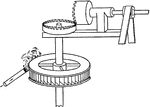
Branca's Impulse Steam Turbine
"In 1629, Branca, an Italian, invented a turbine much like a miniature water wheel, which was driven…
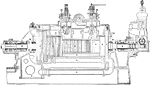
Westinghouse Parsons Turbine Viewed Cross Sectionally
A cross sectional view of Westinghouse Parsons turbine. Steam enters at V and exits at E, turning the…
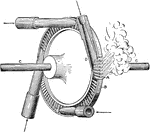
De Laval Steam Turbine
A De Laval steam turbine. The turbine is operated by supplying steam into the four nozzles. The steam…
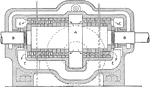
Early Parsons Steam Turbine
"In 1885, Parsons took out his first turbine patent on a motor along the lines previously suggested…
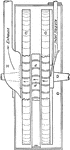
Hartman's Compound Impulse Turbine
"In 1858, Hartman Bros. patented a turbine consisting of two revolving disks c and c' fixed to a shaft…
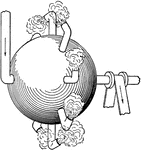
Hero's Simple Steam Turbine
A simple steam turbine by Hero of Alexandra during first century AD. The turbine consists of a hollow…
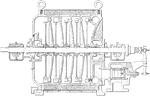
Sectional View of Kerr Turbine
"The shaft, where it passes through the diaphragm, is fitted to a bronze bushing with a few thousandths…
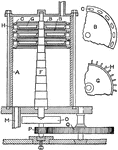
Real and Pichon Compound Steam Turbine
"A compound turbine was patented by Real and Pichon, the idea being to reduce the velocity of rotating…
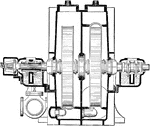
Cross Sectional View of Two Stage Condensing Terry Steam Engine Turbine
A two stage condensing Terry turbine from a steam engine. The steam, entering from the top, rotates…
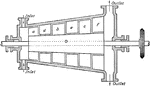
Wilson's Compound Steam Turbine
"A view of Wilson's invention is shown; a, b, and c, are vance which are attached to and rotate with…
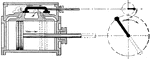
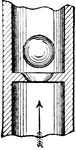
Valve with Lap of Steam Engine Where Steam Enters the Slide Valve Compartment
"The maximum displacement of the valve is attained when the eccentric is horizontal. In this position…
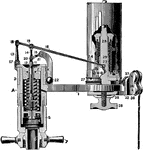
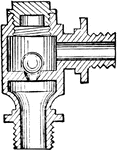
Three Way Pipe Valve for Attaching One Steam Engine Indicator
"If only one indicator is to be used for both ends of the cylinder, it may be connected by side pipes…
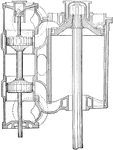
Cross Sectional View of the High Pressure Cylinder of Piston Valve from USS Massachusetts
"This valve consists of two pistons connected by a sleeve through which the valve rod passes. This valve…
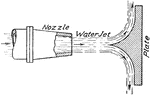
Water Jet Deflected 90 Degrees Measuring Force
"If the velocity of impact of the jet is V feet per second, its velocity in the same direction after…
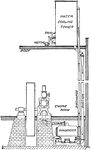
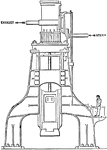
Water Tower Condenser Steam Cooling System in Engine Room
A diagram illustrating cooling steam exhaust of steam engine using a water tower. The water is pumped…
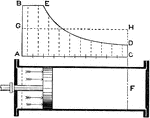
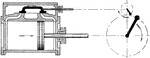
Watt's Work Indicator Diagram
A Watt's work diagram, or indicator diagram, for steam pressure in cylinder. The graph (top) illustrates…