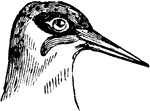
Head of a Green Woodpecker
The head of a Green Woodpecker, a bird belonging to the Scansores order. Scansores is an order of birds,…

Head of a Great Jacamar
The head of a Great Jacamar, a bird belonging to the Scansores order. Scansores is an order of birds,…
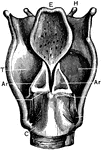
Back View of the Larynx
Labels: T, thyroid cartilage: C, cricoid cartilage; Tr, trachea; H, hyoid bone; E, epiglottis; I, joint…
View of Organs from the Side
The chief organs of the body from the side. Labels: a, arch of the aorta or main artery of the trunk;…

Veins and Arteries of the Body
Chief veins and arteries of the body. Labels: a, place of the heart; the veins are in the back. On the…
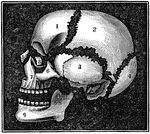
Bones of the Head
A diagram of the bones of the head. Label: 1, frontal lobe; 2, parietal bone; 3, temporal bone; 4, occipital…
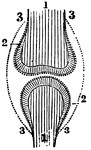
Position of the Bone, Cartilage, and Synovial Membranes
A diagram of the relative position of the bone, cartilage, and synovial membrane. Labels: 1,The extremities…
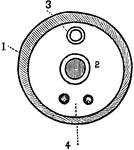
Skeleton of a Cow
A skeleton of a cow shown to illustrate the internal skeleton which all vertebrates share. Labels: 1,…
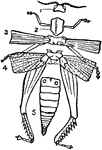
Diagram of the External Structure of an Insect
A diagram of the external structure of an insect. Labels: 1, The head carrying the eyes and the antennae.…
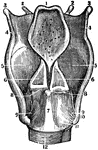
A Back View of the Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx
A back view of the cartilages and ligaments of the larynx. Labels: 1, The posterior face of the epiglottis.…
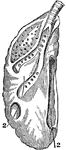
The Right Lung of a Goose
In birds the lungs are confined to the back wall of the chest. They are not separated into lobes, but…
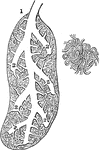
Section of the Lung of a Bird
In birds the lungs are confined to the back wall of the chest. They are not separated into lobes, but…

A Back View of the Brain and Spinal Cord
A back view of the brain and spinal cord. Labels: 1, The cerebrum. 2, The cerebellum. 3, The spinal…
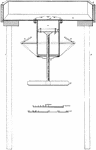
Intrusion Machine
"The principal working parts of the apparatus are the sheet of boiler plate a (fig. 100), the cylinder…
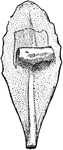
Sedum Leaf
"Leaf of a live-forever (Sedum sp.), with a portion of the epidermis peeled back. Underneath the epidermis…
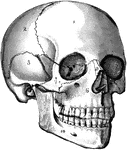
The Skull
The human skull. Labels: 1, frontal lobe; 2, parietal lobe; 3, temporal lobe; 4, the sphenoid bone;…
The Spine
The spine showing the seven vertebrae of the neck, cervical; the twelve of the back, dorsal; the five…
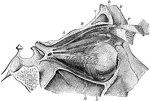
Muscles of the Eye
The muscles of the right eye. Labels: A, superior straight; B, superior oblique passing through a pulley,…
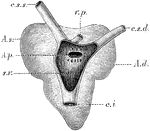
Heart of a Frog
The heart of a frog (Rana esculenta) from the back. Labels: s.v., sinus venosus opened; c.s.s., left…
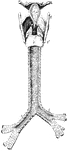
Back View of Respiratory Apparatus
Outline showing the general form of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi, as seen from behind. Labels: h,…
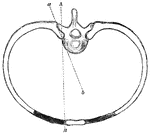
Movement of Ribs
The axes of rotation of rib movement is two; one corresponding with a line drawn through two articulations…

Renaissance Bedstead
The Renaissance bedstead was large in size, it was placed on a podium with a raised head-board. It had…

Renaissance Bedstead
The Renaissance bedstead was large in size, it was placed on a podium with a raised head-board. It had…
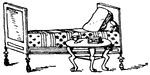
Roman Bedstead
This Roman bedstead had a Pompeian vase-painting. It included a head and foot board. It was made out…

Renaissance Bedstead
This Renaissance bedstead was French and had a cradle head-board with gilt ornaments.
Modern Cane Chair
The cane chair's seat or back is of woven cane-work or padded. The Chair is termed "cane" meaning upholstered.

Modern cane chair
The cane chair's seat or back is of woven cane-work or padded. The Chair is termed "cane" meaning upholstered.

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

German 17th Century Chair
The German 17th century chair had openings for the hand that were carved into the wooden back of the…

Modern Chair
The modern chair's top of the back is horizontal and is crowned with a cornice or an ornament.
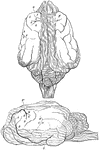
Brain of a Dog
Brain of dog, viewed from above and in profile. F, frontal fissure sometimes termed crucial sulcus,…
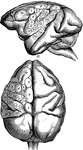
Brain of a Monkey to Show effects of Electric Stimulation
Diagrams of monkey's brain to show the effects of electric stimulation of certain spots. Labels: 1.…
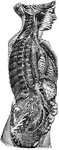
Sympathetic System
Diagrammatic view of the Sympathetic cord of the right side, showing its connections with the principal…
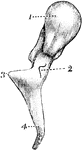
Malleus
The hammer-bone or malleus, seen from the front. 1, the head; 2, neck; 3, short process; 4, long process.
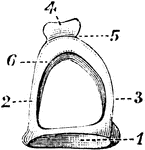
Stapes on Stirrup-Bone
The stapes on stirrup-bone. 1, base; 2 and 3, arch; 4, head of bone, which articulates with orbicular…

Common Chicory
"Chicory (Cichorium Intybus). A, portion of flowering branch; B, basal leaf (runcinate-pinnatifid);…
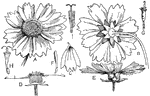
Tickseed
"A composite (Coreopsis sp.). A, B, E, views of the inflorescence or head; C, a ray-flower; D, section…
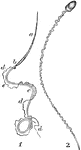
Spermatozoa of a Salamander and Human
Spermatozoa of the salamander (1) and human (2). Labels: a, long pointed head; b, elliptical structure…
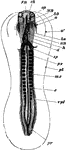
Embryo Chick
Embryo chick (36 hours), viewed from beneath as a transparent object (magnified). Labels:pl, outline…
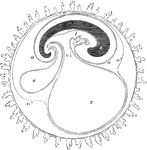
Membranes of the Ovum
Diagrammatic section showing the relation in a mammal between the primitive alimentary canal and the…
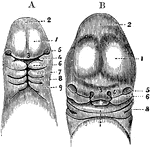
Head of an Embryo
A, Magnified view of the head and neck of a human embryo of three weeks. Labels: 1, anterior cerebral…
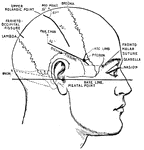
Principle Fissures of the Brain
Showing the lines which indicate the position of the principal fissures of the brain.
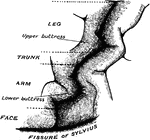
Precentral Gyrus in the Brain
The convolutionary projections of the precentral gyrus, and their relationship to motor areas.
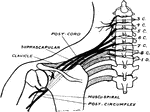
Brachial Plexus
Upper and middle trunks of the brachial plexus viewed from behind to show how depression of the shoulder…
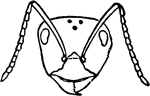
Red Wood Ant Worker's Head
Red Wood Ant worker's head. "Workers supply all the food and are the builders of their wonderful colonies."
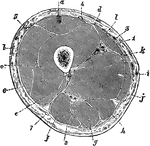
Transverse Section Through the Thigh
Transverse section through the middle of the thigh. Labels: a, Rectus femoris; b, vastus externus; c,…
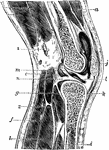
Vertical Section of the Knee Joint
Vertical section of knee joint distended with fluid. Labels: a, Vastus externus; b, crureus; c, short…
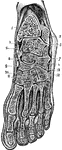
Oblique Anteroposterior Section of
Oblique anteroposterior section of foot, to show the synovial cavities of the tarsus. Labels: 1, tibia;…
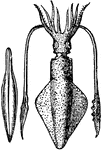
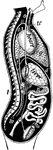
Loligo Vulgaris, with its pen, or internal bone (Lamarck)
"The Common Calmar or Squid. They propel themselves backward through the water with great velocity,…
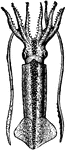
Loligo Gahi (d'Orbigny)
"The Common Calmar or Squid. They propel themselves backward through the water with great velocity,…

Pisa Tetraodon
"Among some Crustaceans there is neither thorax, nor abdomen, nor head, but all three form only one…

The Pipefish (Syngnathus acus)
"The Pipe-fish has the head small, the snout long, nearly cylindrical, slightly raised at the end. The…