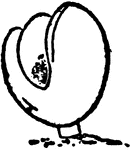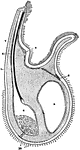
Brachiopoda
Diagrammatic section through an arm of the lophophore of Crania. 1, the lip; 2, the base of a tentacle…
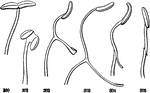
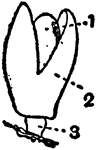
Stamens
Stamens of the mint family. Of a Monarda: the two anther-cells with bases divergent so that they are…
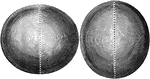
Oblate and Prolate Spheroid
The shape of the earth is that of a round ball or sphere slightly flattened at two opposite sides. Such…

Elizabeth, Countess of Devonshire
This is a line engraving by Sir Anthony Van Dyck. Pictures is Elizabeth, the wife of William Cavendish.…

Charles I Attended by the Marquis of Hamilton
This is a line engraving by Sir Anthony Van Dyck. The picture is one of many done for Charles I. The…
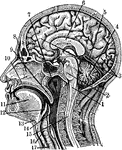
Sectional view of the Head
Section through the Head and Neck on the Median Line. 1. Medulla Oblongata 2. Pons 3. Right lobe of…
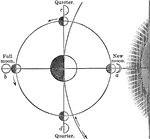
Cause of the Phases of the Moon
During new and full moon, the earth, moon, and sun are all in the same straight line, but, that during…
Five-ranked
Diagram of a shoot with its leaves 5-ranked, with a spiral line drawn from the attachment of one leaf…
Five-ranked
A ground-plan of the 5-ranked shoot; the section of the leaves; a dotted line drawn from the edge of…
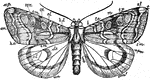
Owlet Moth
Wing of an owlet-moth, with all the markings defined and named.-Right wings: b, basal line; t.a., transverse…
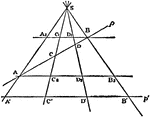
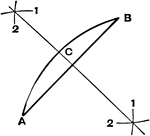
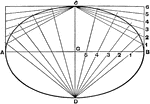
Cross-Ratio Four Points
The cross-ratio of four points in a line is equal to the cross-ratio of their projections on any other…
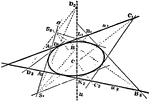
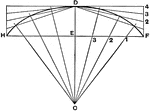
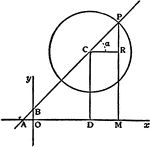
Second Order Curve
Five points are given, of which not three are in a line, a curve of second order may be drawn through…
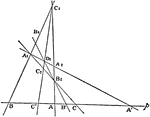
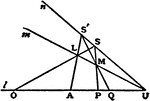
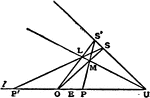
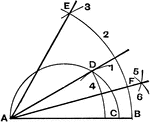
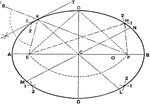
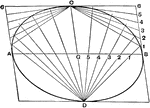
Involution
The three points in which any line cuts the sides of a triangle and the projections, from any point…
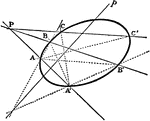
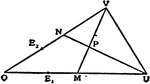
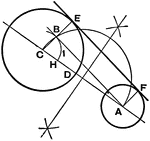
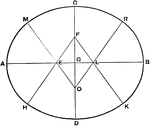
Conic Involution
The lines which join corresponding points in an involution on a conic all pass through a fixed point;…
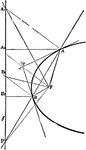
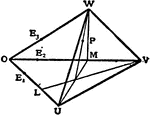
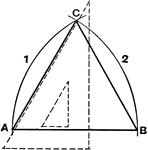
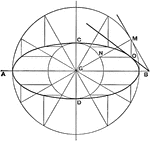
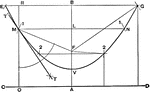
Parabola Foci Properties
The segments between the point of intersection of two tangents to a conic and their points of contact…
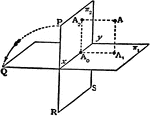
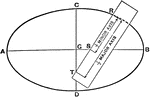
Perpendicular Planes
Two planes lie perpendicular to one another. A line perpendicular to plane 1 and a line perpendicular…
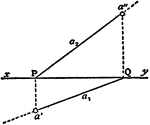
Line Projection
To find the projections of a line which joins two points, A, B given by their projections.
Straight Line
The straight line is the simplest type of locus and the simplest first degree equation.
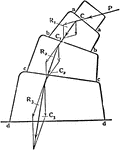
Buttress of Blocks
Uniting the theories of partial polygons of resistance and centres and lines of resistance, this buttress…
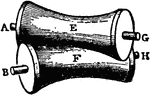
Lateral Sliding Contact
The lines of contact are equal, but the axes are neither parallel to each other, or the line of contact.
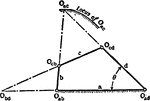
Centrodes
Aronhold stated if any three bodies have plane motion their three virtual centers are three points on…
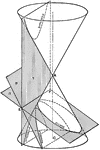
Conic Sections 3D
Three dimensional representation of the intersecting planes required to create the conic sections hyperbola,…
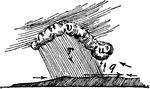
Line squall
"The warmer current ascends, as indicated by the small arrows, and curls at the black wreath (u) of…
Human Sternum Bone
Sternum, front and side view. The sternum, or breast bone, is a flat narrow bone, situated in the median…
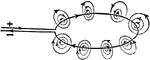
Lines of Force
"Lines of force of a circular loop. If a current flow through the loop in the direction indicated, the…