Kailash Temple
Kailash Temple, also Kailasanatha Temple or Kylas Temple, is one of the 34 monasteries and temples,…

Buddhist Cave Temple at Ellora, Interior
Most famous of the Buddhist caves is a chaitya hall (chandrashala) or 'Vishwakarma cave', popularly…

Indian Pillar from the Rock Temple of Parasona Rama at Ellora
Jain caves reveal specific dimensions of Jain philosophy and tradition. They reflect a strict sense…

Interior of Indra Sabha at Ellora
Jain caves reveal specific dimensions of Jain philosophy and tradition. They reflect a strict sense…

Indian Pillar at Ellora
Jain caves reveal specific dimensions of Jain philosophy and tradition. They reflect a strict sense…

Stupa or Tope
A stupa (from Sanskrit and Pāli: literally meaning "heap") is a mound-like structure containing Buddhist…
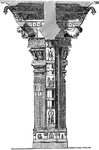
Pillar in Trimal Naik's Tschultri
A pillar is similar to a column which is a vertical support structure in architecture, but the base…

Pagoda
All these buildings are of a pyramidal shape, with vertical stages, which are separated by curved roofs…
Pilaster, Temple of Chillimbaram
All these buildings are of a pyramidal shape, with vertical stages, which are separated by curved roofs…
Pagoda Column
All these buildings are of a pyramidal shape, with vertical stages, which are separated by curved roofs…
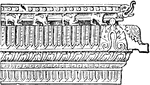
Pagoda Moulding
All these buildings are of a pyramidal shape, with vertical stages, which are separated by curved roofs…

Temple of Chillimbaram Entrance Elevation
All these buildings are of a pyramidal shape, with vertical stages, which are separated by curved roofs…

Sarinda
"Sarinda. A Hindu viol, which has a body made of a single wooden block, elliptical in general contour,…
Indian Matchlock
The Matchlock was the first mechanism or "lock" invented to uncomplicate the firing of a hand-held firearm.

Porcelain Tower at Nankin
Indian art made its entrance into China with the worship of Buddha. But still diversities, corresponding…
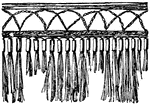
Indian-Mexican Pouch Valence
The Indian-Mexican pouch valence is a hanging textile termination with the lower end ornamentally cut.…

Indian Elephant
The Indian Elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) is an Asian elephant, the largest living land animal in…
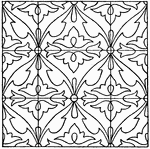
Indian Enamel Pattern
The Indian enamel pattern is a design that uses metal fillets that are filled with pulverized colored…

Indian Enamel Pattern
The Indian enamel pattern is a design that uses metal fillets that are filled with pulverized colored…

Fred Ransom and a Native American
From, Bache's book The Young Wrecker, the boy Fred Ransom defends himself against a Native American…

Osceola, Chief of the Seminoles
Chief Osceola of the Florida Seminole Indians stands proudly at his tribe's village.

Osceola, Chief of the Seminoles
(1804-1838) Osceola was a war chief of the Seminole Indians in Florida, most recognized for his leadership…

Obverse and Reverse Sides of Fanam of Madras
The obverse and reverse sides of the fanam, a small silver coin used in Madras, India.

Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (also known as the Battle of Sharpsburg, particularly in the South), fought on…

William Penn's Treaty with the Native Americans
An illustration of the treaty between the Native Americans and William Penn.

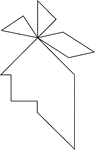
Indian
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
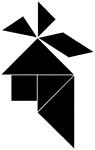
Indian
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
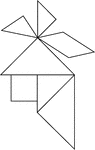
Indian
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…
Indian
Tangrams, invented by the Chinese, are used to develop geometric thinking and spatial sense. Seven figures…

Tokay Gecko
The Tokay Gecko (Gekko gecko) is a lizard in the Gekkonidae family of geckos. It was once known as the…

Indian Darter
"The Indian Darter (Plotus melangaster) or snake-bird of tropical and subtropical America, ranging northwards…

Indian Jacana
"Hydrophasianus chirurgus, the Indian Jacana, of most of the Indian Region, is Bronzy-brown above and…

Female Hornbill Laying Down Feeding Her Young
"Dichoceros bicornis of India and the Malay countries has a large yellowish-red casque, hallowed and…
Native American Rebus
"Eighty armed Pottawattomie Indians surround a house and attack the inmates." -Trowbridge, 1866

Indian Pitta
"Pitta brachyura, the Indian Pitta, has plumage that exhibits vivid scarlet, blue, and green tints,…

Nuthatch
"The colours in Sitta caesia, (Nuthatch) which ranges over nearly all the Palaearctic and Indian Regions,…
Virginia Cut Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…

Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…

Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…
Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…
Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…
Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…
Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…
Indian Rice Grass
Indian Rice Grass (Zizania aquatica), also known as Wild Rice, or Water Oats, is found in swampy borders…

Chinese Sugar Cane
The stem of Chinese Sugar Cane (Sorghum nigrum), also known as Sorgho, or Sorgho Sucre, rises from six…

Indian Corn
Maize known as corn by most English-speakers, is a cereal grain domesticated in Mesoamerica and subsequently…

Indian Corn
Maize known as corn by most English-speakers, is a cereal grain domesticated in Mesoamerica and subsequently…

Indian Corn
Maize known as corn by most English-speakers, is a cereal grain domesticated in Mesoamerica and subsequently…