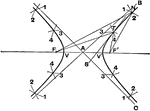
Argonaut, side view
Argonaut, side view submerged, 1901. Key: C-driving wheel, E-rudder and guiding wheel, G-air lock, K-compartment…
Clarinet
The richest instrument in compass and in variety of timbre of all the wind instruments. Its tube is…
Alto Saxhorn
A valved brass wind instruments that resemble the bugle and have a full even tone and wide compass.
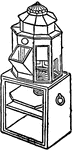
Binnacle
"A Binnacle, corrupted from bittacle, a wooden case or box in which the compass on board a ship is kept…
Tenor Trombone
"The Trombone is a large, deep, and loud-toned instrument of the trumpet kind, the name being an augmentative…
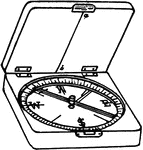
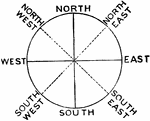
Box compass
"It has four cardinal points, N, E, S, and W marked, as well as a circle graduated in degrees from sero…
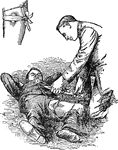
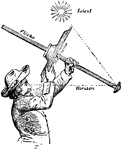
Tourniquet
"The principal of a tourniquet is easily understood, a pad or compass placed on the line of the artery…
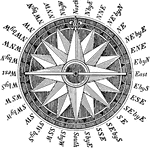
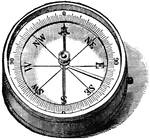
Compass
A instrument used for navigation. The needle is magnetic and always points to the north pole.
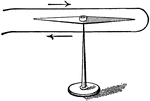
Needle, compass
"Bring the two ends of the wire into contact, and thus close the circuit. The needle instantly flies…
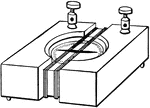
Galvanoscope
"Secure the two ends of the wire by double-pointed tacks. Place a small pocket compass upon the block…

Dipping needle
"A small bar magnet suspended in such a manner as to allow it to assume its chosen position relative…

Globe
An illustration with multiple instruments used for navigation. These items include a globe, compass,…

Dipping Compass
An instrument consisting essentially of a dipping needle, a verticle graduated circle whose center coincides…
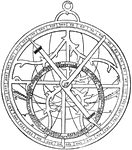
Regiomontanus' Astrolabe
A historical astronomical instrument used to predict positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars.
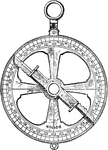
Later Astrolabe
A historical astronomical instrument used to predict positions of the Sun, Moon, planets and stars.
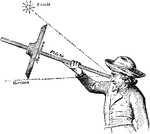
Jackstaff
An instrument which could more readily adapt itself to the swaying of the observer's body in a sea-way,…
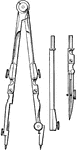
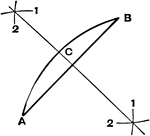
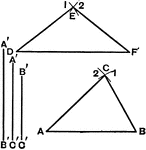
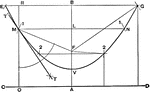
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
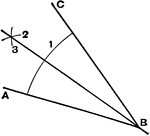
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
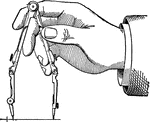
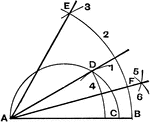
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
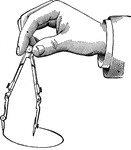
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
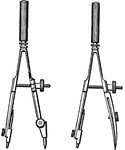
Compasses
"The compasses, next to the T square and triangles, are used more than any other instrument. A pencil…
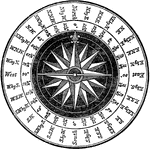
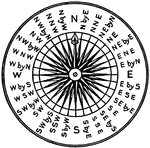
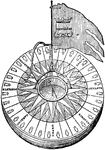
Compass Card
"Three principal parts, the card, the needle on its lower suface, and the case. The whole is enclosed…

Compass Card
"Plan and Transverse Section of Sir William Thomson's Compass-card. B, Corrector for quadrantal error;…
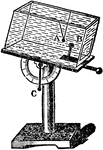
Sine Electrometer
"The sine electrometer of August, is a modification of the single pendulum electroscope, analogous in…

Compass
"Compass, Mariner's, is the name given to the instrument by which sailors are enabled to steer their…
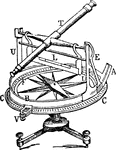
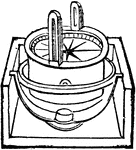
Declinometer
"Upon a tripod provided with levelling screws stands the pillar P, to which is fixed the graduated azimuthal…
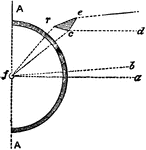
Straight Prisms
"Condensing Straight Prisms.—These, either by reflexion or refraction or both, cause a ray fr…
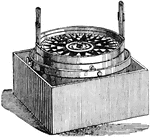
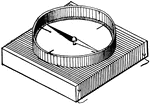
Azimuth Compass
A compass placed in some convenient part of a ship on the midship line and provided with vanes, screws,…

Azimuth Compass
"At sea the declination is generally observed by means of an azimuth compass invented by Kater. It consists…

Still Life with Globe and Telescope
Still life arrangement including a globe, telescope, book, right angle, rolled map, and dividers.
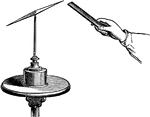
The Magnetic Needle
If a magnetized bar or needle be suspended at its centre of gravity so as to move freely in a horizontal…
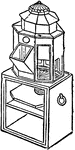
Binnacle
A wooden case or box in which the compass on board a ship is kept to protect it from injury. A light…

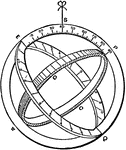
Gyroscope
Three suspended concentric circles free to move independently of each other at right angles.
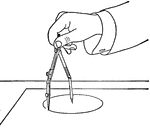
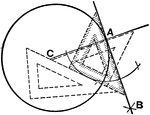
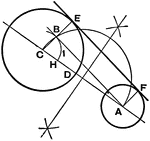
Dividers
Hairspring dividers are for creating bisectors of circles. They are similar to a compass, but with two…
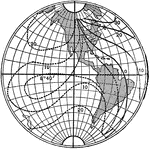
Isogonic Lines of Earth
"The magnetic poles of the earth do notc oincide with its geographical poles and, condequently, in some…