Clipart tagged: ‘archenteron’
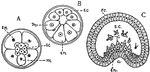
Mesoderm
"Modes of forming mesoderm. A and B, special mesoblasts distinguishable early in egmentation (annelid):…
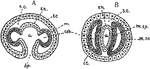
Mesoderm Forming
"Mesoderm formed by pouches from entoderm after gastrulation. A and B, early and later stages in formation…
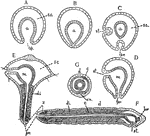
Polygordius
"Diagrams of stages in the metamorphosis of Polygordius, a primitive annelid. Ectoderm throughout is…
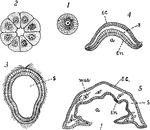
Simple Sponge Development
"Diagrams to illustrate the development of one of the simpler types of sponge: I, the egg; 2, section…