Clipart tagged: ‘arthropods’
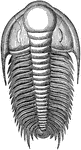
Paradoxides Harlani
Paradoxides was a genus of relatively large trilobites, extinct marine arthropods, that form the class…

Arachnid Scorpion
The name of animals of the class Arachnida. Scorpions have an elongated body, suddenly terminated by…

Centipede
Centipedes are arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda and the Subphylum Myriapoda. They are elongated…

Scorpion
Scorpions are any arachnid of the order Scorpionida. Unlike the majority of arachnid species, scorpions…
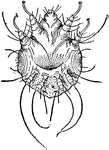
Itch Mite
The itch mite (Sarcoptes) is a genus of skin parasites, and part of the larger family of mites collectively…
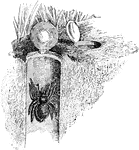
Trapdoor Spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing chelicerate arthropods. Trapdoor spiders, of family Ctenizidae,…
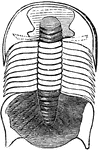
Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Why the trilobites…
Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Why the trilobites…

Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita.The earliest…