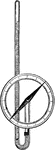Clipart tagged: ‘Atmospheric’
Atmospheric Pressure
"The pressure of the atmosphere may be easily shown by the tube and piston. suppose there is an orifice…

Mercury Barometer
"Mercury enclosed in a tube inverted and inserted into a bath of mercury can serve as a measurement…
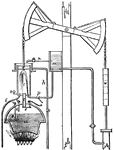
Newcomens Engine
"The simple outline of the atmospheric engine. Its mode of operation is as follows. Steam is admitted…
Atmospheric and Forcing Pump
"A curious combination of the atmospheric pump and the forcing pump, invented by Mr. Trevethick." -Comstock…
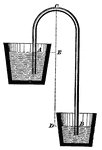
Siphon
"The action of the siphon illustrates the effect of atmospheric pressure. It is simply a bent tube having…