Clipart tagged: ‘bronchial tubes’
Bronchial Tubes Terminating in Air Vesicles
View of the bronchial tubes, terminating in air vesicles. On the left is the external view (1, bronchial…
Bronchioles
This diagram shows the bronchial tubes, with clusters of cells. The bronchioles are the first airway…
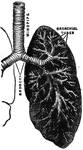
Respiratory Mechanism
"The respiratory mechanism consists of the lungs, a series of minute air chambers with a network of…
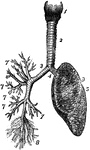
Respiratory System
The respiratory system. Labels: 1. the larynx; 2. the trachea; 3. right bronchia; 4. left bronchia;…