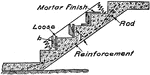
Clipart tagged: ‘concrete’
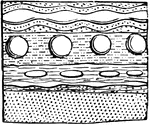
Concretionary Structure
This illustration shows a rock made up of all kinds of concretionary objects.
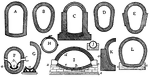
Collection of Sewer Cross-Sections
"A conduit or canal constructed, especially in a town or city, to carry off superfluous, water, soil,…
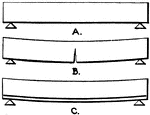
One-Course Work
"Single-course pavement is usually made five inches thick. Proportions for this should be 1:2:3. Concrete…
Two-Course Work
"For two-course floors and pavements, a concrete base of about four inches thick, mixed 1:3:5 (that…