Clipart tagged: ‘cosine’
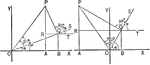
Sum of 2 Acute Angles
Illustration of two triangles, showing the sine of the sum of two acute angles expressed in terms of…
Unit Circle
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. The…
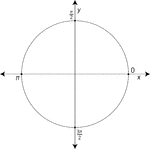
Unit Circle Labeled At Quadrantal Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
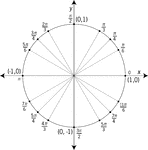
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
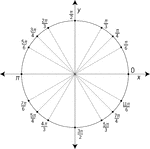
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
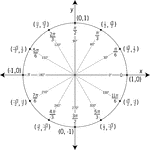
Unit Circle Labeled In 30° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
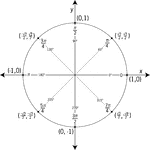
Unit Circle Labeled In 45 ° Increments
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
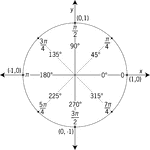
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
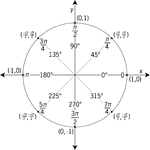
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
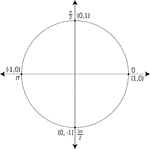
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
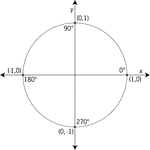
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
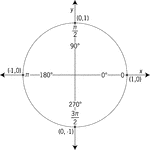
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
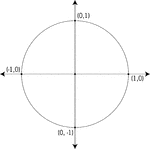
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. At each…
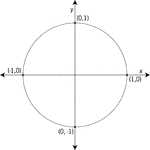
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
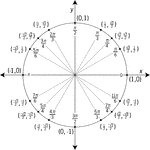
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
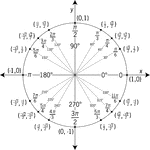
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
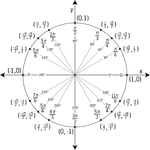
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
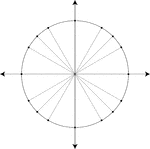
Unit Circle Marked At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
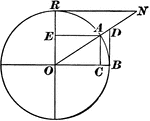
Versedsine and Coversedsine in Circle
The coversedsine is equal to 1 minus the sine. In this figure, AE is parallel to OB; hence, EO = AC…
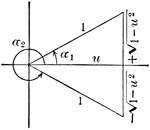
Angle Expressed As An Inverse Function
Illustration that can be used to show that when given an angle, expressed as an inverse function of…
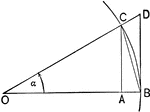
Triangles and Sectors in Quadrant I
Illustration of an angle &alpha with the vertex at the center, O, of a circle with radius OB. AC and…
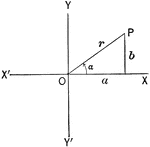
Triangle in Quadrant I
Illustration of an angle &alpha with the terminal side used to draw a triangle in quadrant I.
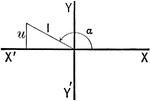
Triangle in Quadrant II
Illustration of an angle with the terminal side used to draw a triangle in quadrant II.
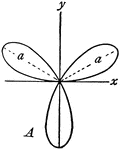
Rose
"In geometry, certain transcendental curves having, in polar coordinates, equations of the form ρ…
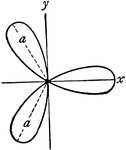
Rose
"In geometry, certain transcendental curves having, in polar coordinates, equations of the form ρ…
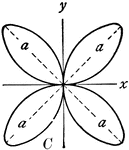
Rose
"In geometry, certain transcendental curves having, in polar coordinates, equations of the form ρ…
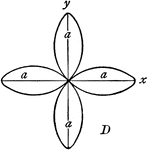
Rose
"In geometry, certain transcendental curves having, in polar coordinates, equations of the form ρ…
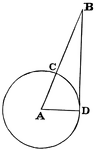
Circle with Secant
A secant is "a line which cuts a figure in any way. Specifically, in trigonometry, a line from the center…
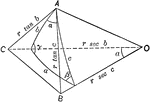
Relationships In A Spherical Triangle
Illustration used, with the law of cosines, to find the relation between the three sides and an angle…
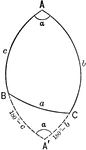
Relationships In A Spherical Triangle
Illustration used to extend the law of cosines when finding the relation between the three sides and…
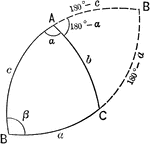
Relationships In A Spherical Triangle
Illustration used to extend the law of cosines when finding the relation between the three sides and…
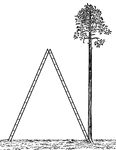
Skyscraper Giant Stepladder
Illustration of a giant stepladder, sometimes called a skyscraper stepladder, that is opened next to…
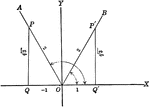
Trigonometric Reference Triangles/Angles (60 degrees) Drawn in Quadrants
Trigonometric reference triangles/angles drawn for 60 degree reference angel in quadrants I and II.
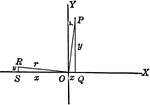
Trigonometric Reference Triangles/Angles Drawn in Quadrants
Trigonometric reference triangles/angles drawn for reference angel in quadrants I and II. This illustration…
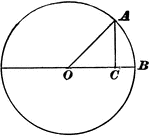
Trigonometry Triangle to Show Sine, Cosine, and Tangent
Right triangle OCA, inside of Circle O is used to show that side AC is "opposite" O and side OC is "adjacent"…