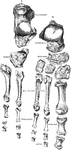Bones of the Foot
"The foot is built in the form of a half-dome or half-arch. This is to afford a broad, strong support…

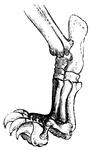
Compressed Foot
An extreme form of a compressed foot, typically seen in the deer and ox. It is useful for land transit.
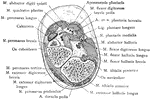
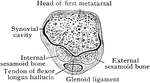
Cross Section Through Tarso-Metatarsal Joint of Foot
Section through the right tarsometatarsal joint. Upper surface.
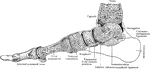
Longitudinal Section Through Foot
Longitudinal section through right foot in axis of first metatarsal bone.
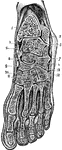
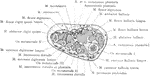
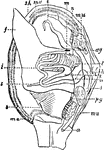
Oblique Anteroposterior Section of
Oblique anteroposterior section of foot, to show the synovial cavities of the tarsus. Labels: 1, tibia;…
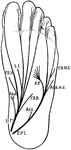
Plantar Nerves of the Foot
Scheme of distribution of the plantar nerves. Labels: I.P1, internal plantar nerve, and its cutaneous…
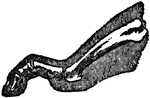
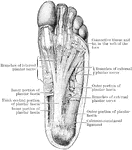
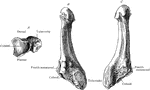
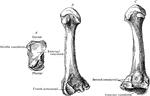
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
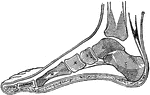
Side View of Bones in Foot
"The Foot is that part of the lower extremity below the leg on which we stand and walk. It is composed…
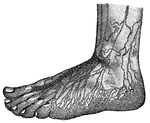
Superficial Lymphatics of the foot
"In nearly every tissue of the body there is a marvelous network of vessels, precisely like the lacteals,…

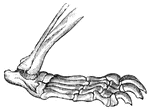
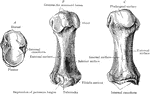
Upper Surface of the Left Foot
Bones of the upper surface of the left foot. Labels: 1, astragalus; 2, its anterior face; 3, os calcis;…
Foot-race
"The Olympic games were of greater efficacy than the Amphictyonic Council in promoting the spirit of…
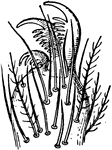
Foot of a garden spider
"Closeup of a garden spider's foot, showing the 'combs' for clinging to webs."—Finley, 1917
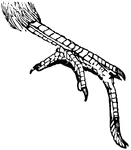
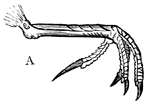
Foot of a Goat-Sucker
The foot of a goat-sucker, with a distinctively longer middle toe, believed to be used for either grasping…
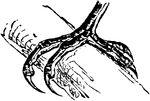
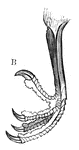
Foot of a Great Jacamar
The foot of a Great Jacamar, a bird belonging to the Scansores order. Scansores is an order of birds,…
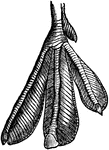
Foot of Grebe
"In this foot each toe is provided with its swimming membrane; the membrane being closed when the foot…
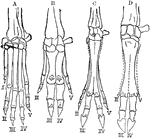
Hands of Vertebrates
A comparison of vertebrate hands. A, hand or anterior foot of the dog; B, that of the hog; C, that of…
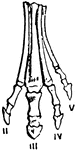
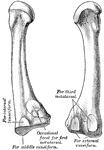
Horse Foot
"Successive stages of modification of the feet of extinct forms of horse-like animals, showin gradual…
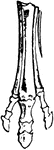
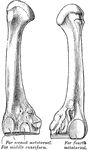
Horse Foot
"Successive stages of modification of the feet of extinct forms of horse-like animals, showin gradual…
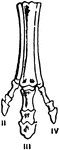
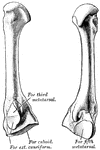
Horse Foot
"Successive stages of modification of the feet of extinct forms of horse-like animals, showin gradual…
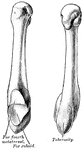
Horse Foot
"Successive stages of modification of the feet of extinct forms of horse-like animals, showin gradual…
Horse Foot
"Successive stages of modification of the feet of extinct forms of horse-like animals, showin gradual…

Pagan Lamp in the Shape of a Foot
"A pagan votive lamp of bronze, now in the museum at Naples." -Bodmer, 1917
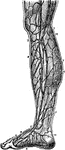
Veins of the Leg
Veins of the leg. Labels: 1, saphenous; 2, collateral branch; 3, anastomosis; 4, internal saphenous;…
Mollusc Anatomy
"Anatomy of an Acephalous Mollusc (Mactra): s, stomach; ii, intestine; ag, anterior ganglions; pg, posterior…
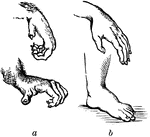
Comparison of the Hand and the Foot of a Monkey and Human
The power possessed by the hand of a human is chiefly depended upon the size and power of the thumb,…
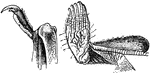
Mystacina Tuberculata
"Thumb and leg and foot of Mystacina tuberculata." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903
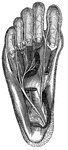
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Plantar) and its Branches which supply the Bottom of the Feet. Note the cut tendons…
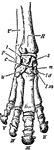
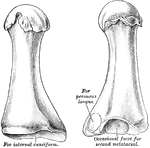
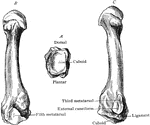
Perissodactyle
"Bones of the fore foot of existing Perissodactyle. Tapir (Tapirus indicus)." —The Encyclopedia…
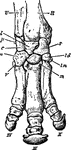
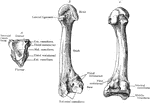
Perissodactyle
"Bones of the fore foot of existing Perissodactyle. Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros Sumairensis)." —The…