Lantern Holder
A lantern is a portable lighting device used to illuminate broad areas. Lanterns may be used for signaling,…
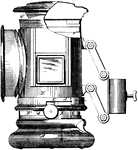
Bicycle Lantern Illumination
The earliest bicycle and car lights were powered by acetylene, generated in a carbide lamp, now almost…
Light Fixture
A lamp is a replaceable component such as an incandescent light bulb, which is designed to produce light…
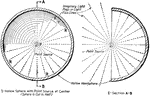
Light Intensity
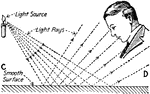
"The radiation of light, or the intensity of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance…
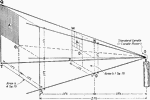
Light Intensity Versus Distance
"Another illustration of how luminous density varies inversely as the square of the distance." —Croft…
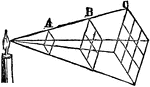
Light Intensity at Different Distances
"A card placed at point A receives normal light. At point B the card receives four times as much light,…
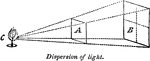
Dispersion of Light
"The intensity of light from a candle decreases proportionally with an increase in distance from the…

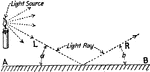
Rays of Light
"Rays of light are said to diverge, when they proceed from the same point, and constantly recede from…
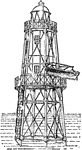
Lighthouse
"An iron pile light erected at Haneda, in the Bay of Yedo, Japan." —The Encyclopedia Britannica,…

Gas Lighting
Lamps using natural gas to produce light. Uses convention make the lamp very efficient.
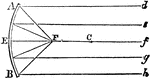
Reflection from Concave Mirrors
"Parallel rays of light strike the concave mirror. The rays converge at the focus, F, which is halfway…
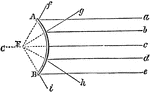
Reflection by Convex Mirrors
"Parallel rays strike the convex mirror, reflect, and diverge as if they had originated from a virtual…
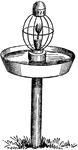
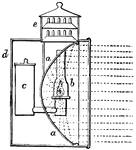
Moth Lantern
From the well known nocturnal habits of moths, and the certainty of their being destroyed by a light,…
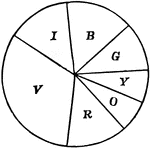
Newton disk
"Make a 'Newton disk', painting the prismatic colors in proper proportion as indicated." — Avery,…
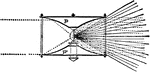
Parabolic Profile
"In order strictly to equalize a fixed light over the whole horizon, which could not possibly be done…
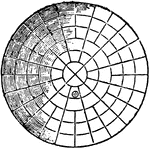
Parabolic Reflector
"In 1763, or at latest before 1777, parabolic reflectors were first used for lighthouse illumination…
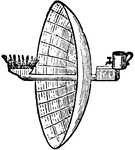
Parabolic Reflector
"In 1763, or at latest before 1777, parabolic reflectors were first used for lighthouse illumination…
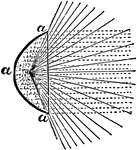
Paraboloid
"It will be seen that the parabolic mirror a is at best but a very imperfect instrument, for even if…

Paul and Silas in Jail - the Jailer Kneels Before Paul
"And the jailor, being roused out of sleep and seeing the prison doors open, drew his sword and was…

Descent of the Holy Spirit on the Apostles
"And suddenly there came from heaven a sound as of the rushing of a mighty wind, and it filled all the…
Prism
"A prism is a piece of glass, having for its sides three plane surfaces and for its ends two equal and…
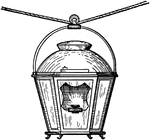
Réverbère Oil Lamp
"The first Réverbère --oil lantern-- with a metal reflector, used to light the streets…
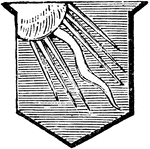
Ray of Sun
"Azure, a ray of the sun issuing out of the dexter corner of the escutcheon. The lines on each side…

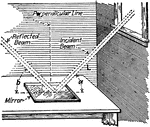
Reflected Light
"The apparatus shown is used to prove that incident rays and reflected rays are equal." -Avery 1895
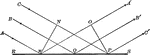
Explanation of Reflection
"Consider a beam of light as made up of a number of ehter waves moving forward in air and side by side,…
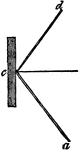
Reflection of Light
"Thus, if a sunbeam, passing through a small aperure in the window shutter a, be permitted to fall upon…
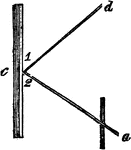
Reflecion of Light
"Let a ray pass towards a mirror in the line a, c, it will be reflected off in the direction of c, d,…
Reflection of Light
"The ray a, c, is the ray of incidence, and that from c, to d, is the ray or reflection. The angles…
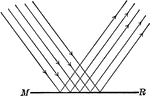
Regular Reflection
"Regular reflection results from the incidence of radiant energy upon a polished surface. When a beam…
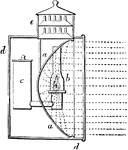
Parabolic, Reflector
A polished surface of metal, or any other suitable material, applied for the purpose of reflecting rays…
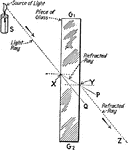
Refraction of Light through Glass
"Illustrating refraction of light from a source through glass, and the appropriate angles of refraction."…
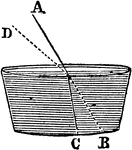
Refraction Between Mediums
"Since air is a rarer medium and water is denser, as ray A passes into the water, it is refracted to…
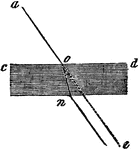
Refraction of Light
"Although a ray of light will pass in a straight line, when not interrupted, yet when it passes obliquely…
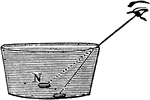
Refraction as seen by the Human Eye
"If the coin were to be observed in an empty pan and then watched as the pan was filled with water,…
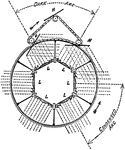
Repeating Light
"Plane mirrors M revolve on an endless chain placed outside of the apparatus and alter the direction…
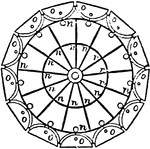
Revolving Light
"In order to produce, on the catoptric system, a fixed light showing all round the circle, a number…
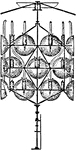
Revolving Light
"If again the light was to revolve, then a revolving chandelier was employed having a certain number…

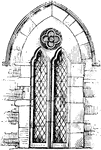
Lantern Tower at St. Ouen; Rouen, France
In Gothic architecture, a lantern tower is frequently placed over the center of cross churches, and…

Railroad Semaphore
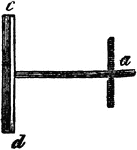
"Railway Semaphore. a, lever, which operates both b, blade, and c, lantern." -Whitney, 1911
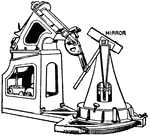
Siderostat
"An instrument described by Foucault for transmitting a beam of light along the optical axis of a fixed…
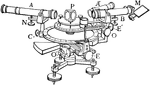
Spectrometer
"An instrument used chiefly to measure the angular deviation of light rays in passing through a prism,…
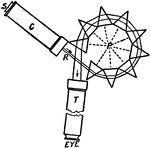
Spectroscope
"C. Collimator; P, center of group of prisms; T, telescope; s, slit through which the ray of light enters,…
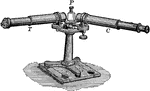
Spectroscope
"A spectroscope is an instrument used ot produce a spectrum of the light form any source, and for its…
Color Spectrum
"A prism is used to disperse ordinary light, and slits are cut in paper S to only allow yellow and blue…
Visible spectrum
"A spectrum of sunlight is crossed by dark lines, many hundreds of whcih have been counted and accurately…
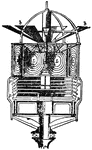
Stevensons Revolving Light
"In 1835 Mr. Stevenson, in a report to the Northern Lighthouse Board, proposed to add fixed reflecting…
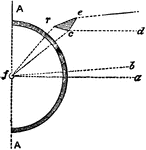
Straight Prisms
"Condensing Straight Prisms.—These, either by reflexion or refraction or both, cause a ray fr…