Clipart tagged: ‘negative’
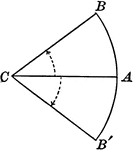
Positive and Negative Arcs in Circles
Illustration showing arcs measured in positive and negative angles.
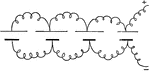
Parallel Connection
"When all of the positive plates are connected on one side, and all of the negative plates are connected…
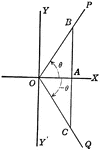
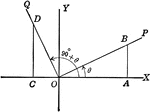
Coordinate Axis With Perpendiculars Drawn To Form Similar Right Triangles From Positive and Negative Theta, Θ
Angle XOP=Θ and angle XOQ=- Θ. From a point in the terminal side of each a perpendicular line is drawn…
Coordinate Axis With Perpendiculars Drawn To Form Similar Right Triangles
Angle XOP=Θ and angle XOQ=90+Θ. From a point in the terminal side of each a perpendicular line is…
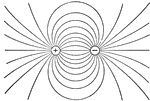
Electricity
This illustration shows the field between two equally and oppositely charged spheres, mapped out by…
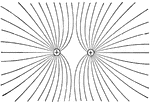
Electricity
This illustration represents the field between two equal positive charges; in this case the lines of…
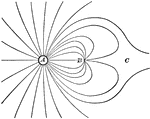
Electricity
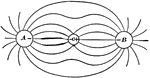
This illustration shows the lines of force when a positive charge equal to 4 at A, and a negative charge…
Electricity
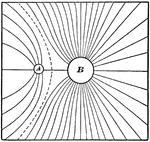
This illustration shows the field of force due to a charge 1 at A, and a like charge 4 at B.
Electricity
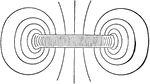
This illustration shows the field of force between two parallel planes. At the edges its lines of foce…
Electricity
A is a positively charged conductor and B represents the equal and oppsite charge. When the conductor…
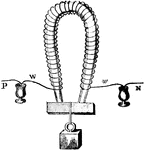
Magnet
"The coils of wire may begin near one pole of the magnet and terminate near the other, or the wire may…
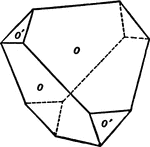
Positive and Negative Tetrahedron in Combination
This form shows a positive and negative tetrahedron in combination.
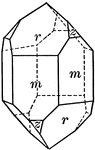
Quartz
"Terminated usually by a combination of a positive and negative rhombohedron, which often are so equally…
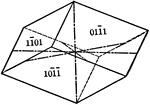
Negative rhombohedron
"The rhombohedron is a form consists of six rhombic-shaped faces, which correspond in their position…
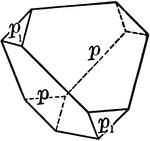
Sphenoid, positive and negative
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…

Negative tetrahedron
"The tetrahedron is a form composed of four equilateral triangular faces, each of which intersects all…
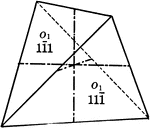
Positive and negative tetrahedrons
"If a positive and negative tetrahedron occured together with equal development, the resulting crystal…