Clipart tagged: ‘ovum’
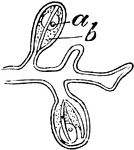
Athorybia Gonophores
"A, female gonophores of Athorybia rosacea on their common stem or gynophore: a, ovum; b, radial canals."…
Cell Development
Every human body begin as a single nucleated cell. This cell, known as the ovum, divides or segments…

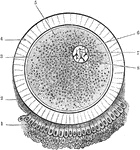
Chorion Villi
Very soon after the entrance of the ovum into the uterus, in the human subject, the outer surface of…
Ovum
The ovum and its coverings. The corona radiata, which completely surrounds the ovum, is only represented…
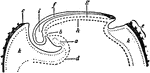
Developing Ovum
Diagram of a developing ovum, seen in longitudinal section. Labels: a, pericardium; b, bucco-pharyngeal;…
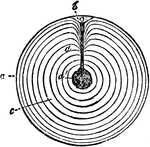
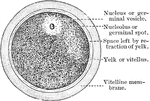
Fowl Ovum
"Meroblastic ovum (yelk) of domestic fowl, bat. size, in section; after haeckel. a, the thin yelk-skin,…

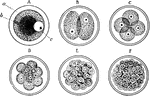
Maturation of the Ovum
The maturation of the ovum. A, An ovum at the commencement process. B, After the formation of the spindle.…
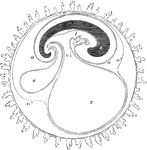
Membranes of the Ovum
Diagrammatic section showing the relation in a mammal between the primitive alimentary canal and the…
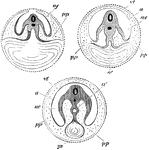
Development of the Yolk Sac
Diagram showing the three successive stages of development. Transverse vertical sections. The yolk sac,…