Clipart tagged: ‘pavement’
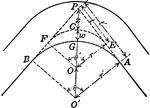
Curve in Pavement of Road
Illustration of blueprint used by highway engineers to widen the pavement on the inside of the curve…
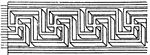
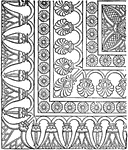
Parallel Fret Band
The parallel fret band is a pattern that is parallel in perspective that was found in a Roman mosaic…

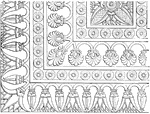
Grotesque Italian Majolica
The Italian Majolica Grotesque is designed on a pavement, made out of fine italian glazed earthenware.…

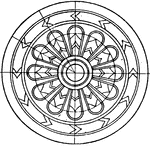
Assyrian Pavement Square Panel
The Assyrian pavement square panel is a divided into eight equal spaces that are decorated with a repeated…
One-Course Work
"Single-course pavement is usually made five inches thick. Proportions for this should be 1:2:3. Concrete…
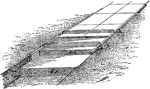
Two-Course Work
"For two-course floors and pavements, a concrete base of about four inches thick, mixed 1:3:5 (that…