Clipart tagged: ‘piston’
Piston and Rod
"A piston and rod shown with attached weight. The valve, A, can be opened and closed as needed so that…
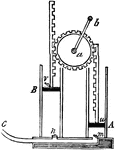
Air Pump
"The piston rods are furnished with racks, or teeth, and are worked by the toothed wheel a, which is…
Atmospheric Pressure
"The pressure of the atmosphere may be easily shown by the tube and piston. suppose there is an orifice…
Barometer
"Suppose a to be a long tube, with the piston b so nicely fitted to its inside, as to work air tight.…
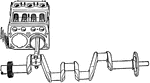
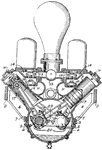
Building an Automobile, Step 03: Cylinders Showing Piston and Crankshaft
"Cylinders showing piston in place and connected to crankshaft. Gasoline vapor is exploded in the cylinders.…
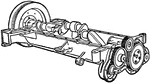
Building an Automobile, Step 04: Cogwheels
"The gears or 'cogwheels' are for running the fan, the pump and other parts." -Bodmer, 1917
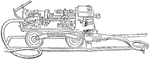
Coal-cutting Machine
"This machine consists essentially of a horizontal piston and cylinder engine fixed upon a platform…
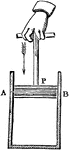
Compressibility of Air
"Let P be a piston, fitted, air-tight, to the cylinder AB. As the piston is driven down, the air, unable…
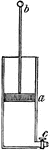
Compression Experiment
"If the strong tube, or barrel, be smooth, and equal on the inside, and there be fitted to it the solid…
Condenser
"The operation of the condenser is the reverse of that of the air pump, and is a much more simple machine.…
Condenser
"Air is pumped down through shaft A through a downward opening valve into a given chamber. Connector…
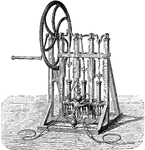
Connected Pumps.
This figure consists of three pumps, the piston rods of which are jointed to three cranks on a horizontal…
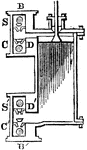
Double-acting Cylinder
"The first alteration to be noticed in the double-acting engine is that of the cylinder. To insure its…
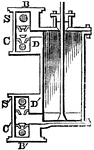
Double-acting Cylinder
"The first alteration to be noticed in the double-acting engine is that of the cylinder. To insure its…
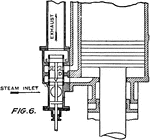
Valve Casing of a Double-column Hammer
"A section through the valve casing of a double-column hammer, fitted with a valve v provided with three…
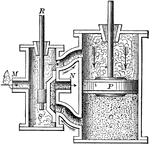
Steam engine
"The steam engine is a powerful device for utilizing the energy involved in the elasticity and expansive…
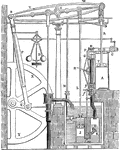
Watt's Double-Acting Condensing Steam-Engine
"Used a boiler to produce steam, chambers to condense it, and drive the pistons of the engine." —Quackenbos…
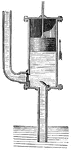
Force pump
"The operation of the force-pump is similar to that of the suction-pump. The outlet-valve generally…
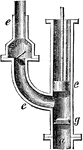
Forcing-Pump
"In the forcing-pump atmospheric pressure plays but a small part. There is no valve in the piston c,…
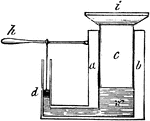
Hydraulic Press
"The pump barrel, a, b, is represented as divided lengthwise, in order to show the inside. The piston,…
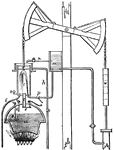
Newcomens Engine
"The simple outline of the atmospheric engine. Its mode of operation is as follows. Steam is admitted…
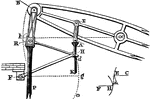
Parallel Motion
"Its mechanism may be understood by the means of the subjoined figure, B represents the end of the beam,…

Pascal's Law and Water Pressure
"...let the area of the piston a be 1 square inch; of b, 40 square inches. According to Pascal's law,…
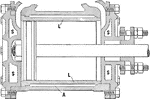
Jacketing Piston to Reduce Heat Loss
"The cylinder covers are also made hollow to permit a circulation of live steam. A cylinder having the…
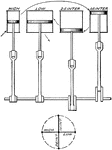
Quadruple Expansion Engine Piston
A piston system from a quadruple expansion engine showing the movement of steam. Steam first enters…
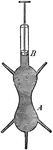
Pressure of Liquids
"The tightly fitted piston at the top of a glass vessel of water is driven down. The contained liquid…
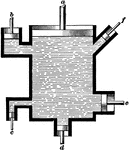
Water Pressure Demonstration
"Let the are of the piston a be 20 square inches; of b, 7 sq. in.; of c, 1 sq. in.; of d, 6 sq. in.;…
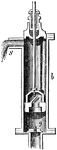
Pump
"The common pump consists of a hollow tube, the lower part of which, descending into the water, is called…
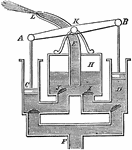
Fire Engine Pump
"Liquid is drawn up pipe F by pistons C and D. Once the liquid passes through the first set of valves,…
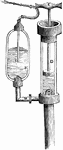
Forcing Pump
"Liquid is drawn up the pipe through the valve H. Piston G pushes the liquid through pipe, M, and into…
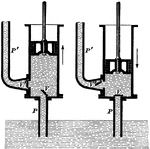
Forcing Pump
"As the piston ascends, as shown in the left-hand figure, the pressure of the atmosphere forces the…
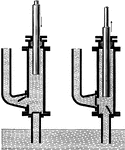
Plunger Pump
"The action does not differ in any way from that of the piston force pump. During the up stroke of the…
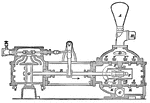
Steam Pump
A typical steam pump. A steam pump is a force pump operated by steam acting on the pistons of a steam…
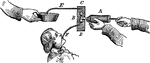
Stomach Pump
"The stomach pump injects liquid into a poisoned person's stomach and then withdraws the liquid and…
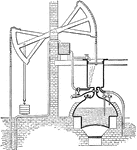
Newcomen Atmospheric Steam Engine
An illustration of Newcomen atmospheric steam engine. The boiler heats the water to build up steam in…
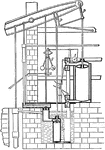
Watt's Final Steam Engine Design
The illustration showing Watt's final steam engine design. The engine is fitted with series of rods…
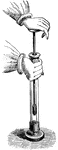
Fire syringe
"Place a bit of tinder in the cavity of the piston of the 'fire-syringe'. Put the piston into the open…