Clipart tagged: ‘potentiometer’
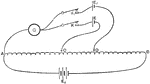
Potentiometer
A potentiometer instrument for measuring the potential (or voltage) in a circuit taps off a fraction…
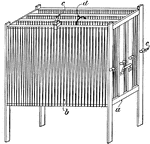
Rheostat
"Nichols Rheostat. a, wooden frame; b, tinned iron strip; c, stationary, and c', movable binding-posts;…