Clipart tagged: ‘quadrants’
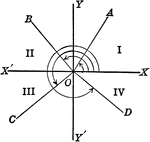
Reference Angles/Triangles Formed by Angles in Quadrants
Lines drawn to horizontal to form triangle ratios (reference triangles, angles).
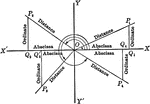
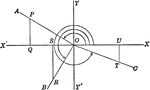
Reference Angles/Triangles Formed by Angles in Quadrants With Labels
Lines drawn to horizontal to form triangle ratios (reference triangles, angles). Axes, quadrants, abscissa,…
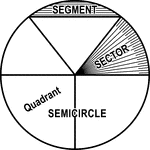
Circle with Segment, Semicircle, Sector, Quadrant, and Central Angle
Illustrations of a circle with segment, semicircle, sector, quadrant, and central angles drawn.
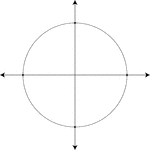
Unit Circle
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. The…
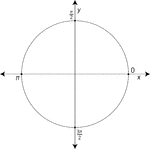
Unit Circle Labeled At Quadrantal Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
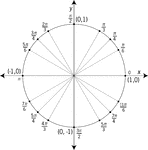
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
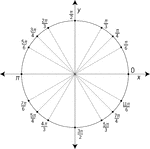
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
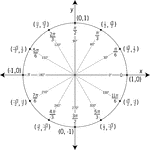
Unit Circle Labeled In 30° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
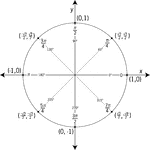
Unit Circle Labeled In 45 ° Increments
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
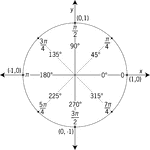
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
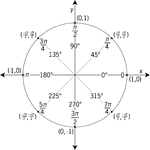
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
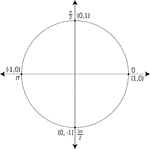
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
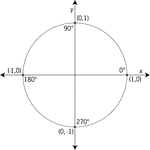
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
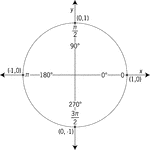
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
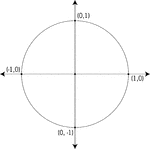
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. At each…
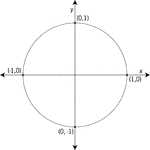
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
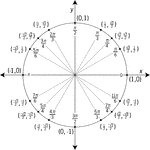
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
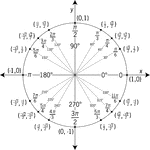
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
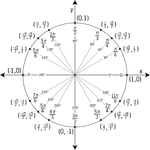
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
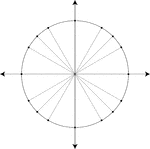
Unit Circle Marked At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
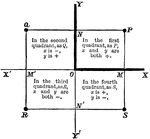
Coordinate Plane
A coordinate planes with the quadrants labeled showing which value (x or y) is positive or negative.
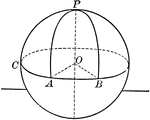
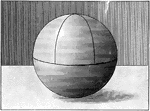
Sphere With Quadrants and Poles
A sphere with quadrants and poles. "A point on the surface of a sphere, which is at the distance of…