Clipart tagged: ‘Stratum’
Eozoic Strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural: strata) is a layer of rock or soil with internally…
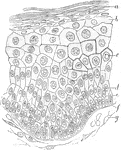
Epidermis
Vertical section of epidermis of the prepuce. Labels: a, stratum corneum, of very few layers, the stratum…
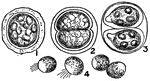
Protococcus
A genus of single-celled algae often forming a yellowish-green stratum on trees' damp walls, and in…

Sandy Stratum
"A sandy stratum, a a, acting as a filter, occupies an inclined position between two other strata impervious…
Simple Springs
Simple or surface springs: (d) stratum, (e) clay, (c) pervious bed, (a) strata, (b) valley.

Strata with Fault Line
An illustration of strata bent at a line of fault. In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural:…

Thallus
"Section of Stratified Thallus of Ricasolia herbacea. a, cortical stratum; b, gonidial stratum; c, medullary…