Clipart tagged: ‘vision’
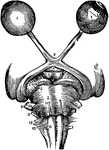
Detection of Astigmatism
Lines for the detection of astigmatism. "The refracting surfaces of the eye acting together are equivalent…
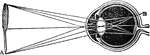
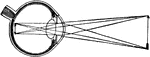
Convergence of Rays in the Aqueous Humor of the Eyeball
The convergence of light rays in the eyeball begins in the aqueous humor is perfected in the crystalline.…

Cornelius the Centurion is Visited by an Angel
"Now there was a certain man in Caesarea, Cornelius by name, a centurion of the band called the Italian…
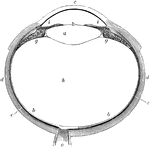
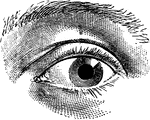
Eye
The human eye. Labels: a, crystalline lens; b, retina; c, cornea; d, sclerotic; e, choroid; g, ciliary…
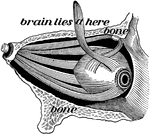
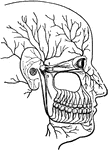
The Eye and its Muscles
The eye and its muscles. Labels: o, the nerve of sight; a, one of the muscles of the eye.
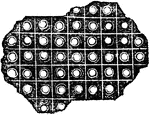
Eye of the Butterfly
Eye of the phalaena or butterfly, magnified, consisting of 11,300 square sections. The eye of the mordella…
Eye of the Yellow Beetle
Eye of the yellow beetle magnified, composed of 8,820 hexagonal cylinders, the interior of each tube…
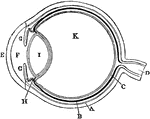
Diagram of the Eye
Plan of the eye seen in section. Labels: A, The Sclerotic Coat; B, The Choroid Coat; C, The Retina;…

Lens of the Eye
Lens of the eye. The rays of light are brought nearer together by the lenses of the eye, just as they…

Section of the Eye
Section of the eye magnified, showing the ciliary processes, the pigmentum nigrum, the retina, and the…
Section of the Eye
The vitreous humor and crystalline lens of the eyeball magnified, with the stains of the pigmentum nigrum…
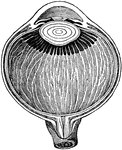
Section of the Eye
Section of the eye magnified, showing the crystalline lens in its proper situation, between the aqueous…
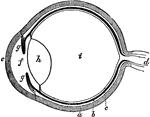
The Eye
The eye. Labels: a, sclerotica; e, cornea; b, choroid; d, optic nerve; f, aqueous humor; g g , iris;…
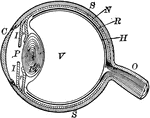
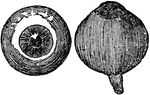
Eyeball
"The most essential parts of human vision are contained in the eyeball, a nearly spherical body, about…
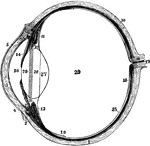
Left Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
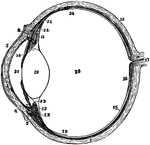
The Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
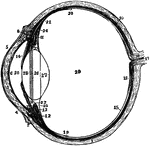
Section of Left Eyeball
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
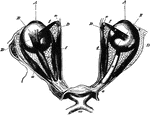
The Eyeballs and Their Muscles
The eyeballs and their muscles as seen when the roof of the orbit has been moved and the fat in the…
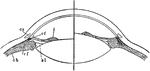
Focusing of the Eye
Diagram to illustrate the mechanism of accommodation (focusing); on the right half of the figure for…

Formation of an Image on the Eyeball
Suppose a person was looking at a church with a tree standing at its side, he would have in each eye…
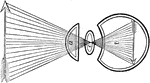
Formation of an Image on the Eyeball
In passing through the crystalline, the rays cross each other, so that those rays which pass from the…
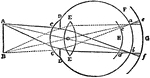
Formation of Circles of Diffusion
An illustration depicting the formation of circles of diffusion. "From point A luminous rays enter the…
Round Safety Glasses
Safety glasses are usually made with shatter-resistant plastic lenses to protect the eye from flying…

Jesus Heals a Man Born Blind
"When he had thus spoken, he spat on the ground, and made clay of the spittle, and anointed his eyes…
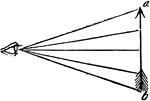
Indistinct Vision
"...where we suppose that the object a, is brought within an inch or two of the eye, and that the rays…
The Use of the Crystalline Lens
A convex lens, bends the ray of light which pass through it, so that they meet at a point called a focus.…

Nearsighted Vision
The lenses and humors of the eye must be very exactly arranged, in order that the sight may be perfect.…

Louis Pasteur
"This picture is based upon a photograph of a painting which has won great fame during recent years.…

Peter Preaches to Jews and Gentiles
Peter preaches to a group of people of different ages, genders, and backgrounds. There are men, children,…
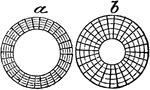
Pupil Contraction and Dilation
On the left (a) the pupil is wide open (dilated), while on the right (b) the pupil is contracted. The…
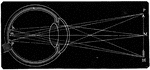
A Diagram of the Retina and Crystalline Lens
A diagram showing how an image is formed upon the retina by the crystalline lens.
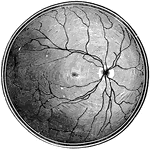
Retina Blind Spot
The right retina as it would be seen if the front part of the eyeball with the lens and vitreous humor…
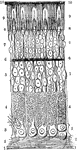
Section of Retina
A section through the retina from it anterior inner surface (1) in contact with the hyaloid membrane,…
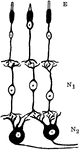
Neurons and Sensory Epithelium in the Retina
Diagram showing relations of the neurons and sensory epithelium in the retina. labels: E, epithelial…
The Structure of the Retina
Next to the choroid and comprising about 1/4 the entire thickness of the retina is a multitude of transparent,…
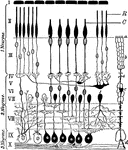
Retinal Structure
Diagram of the structure of the human retina. Labels: I, pigment layer; II, rod and cone layer; R, rods;…

Samuel Meets Eli, the High Priest, at Shiloh
"And the child Samuel ministered unto Jehovah before Eli. And the word of Jehovah was precious in those…
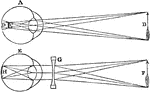
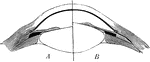
Shortsighted Vision and Correction
A. a shortsighted eye; B. an arrow which it attempts to perceive, but is prevented by the convergence…
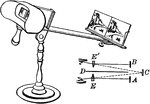
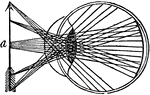
Stereoscope
"The stereoscope is an instrument for illustrating the phenomena of binocular vision, and for producing…
Test type
"The Actual Size of the Test Type, which shiykd be seen by the Normal Eye at a distance of Twenty Feet."…
![An illustration of a transverse section of an ideal eye. "A, summit of cornea; SC, sclerotic; S, Schlemm's canal; CH, choroid; I, iris; M, ciliary muscle; R, retina; N, optic nerve; HA, aqueous humour; L, crystalline lens, the anterior of the double lines on its face showing its form during accommodation; HV, vitreous humour; DN, internal rectus muscle YY', principle optical axis; C, [center] of the ocular globe..." (Britannica, 132).](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/58100/58122/58122_ideal-eye_mth.gif)
Transverse Section of an Ideal Eye
An illustration of a transverse section of an ideal eye. "A, summit of cornea; SC, sclerotic; S, Schlemm's…
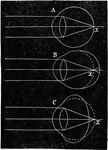
Vision
Diagram illustrating rays of light converging in a normal eye (A), a myopic eye (B), and a hypermetropic…