Clipart tagged: ‘worm stages’
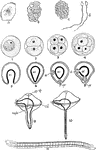
Polygordius
"Development of Polygordius. a., Mother sperm cell; b., c., sperm morulae; d., spermatosoa. 1. Ovum…
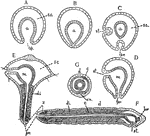
Polygordius
"Diagrams of stages in the metamorphosis of Polygordius, a primitive annelid. Ectoderm throughout is…