Faults
The Faults ClipArt gallery include 37 illustrations and examples of fractures in rocks along which there has been movement. The energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes.

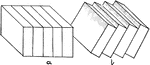
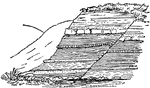
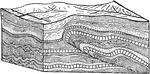
Block Faulting Results
Diagram showing mountains and valleys due to block faulting in the background, and the dissection of…

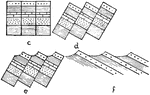
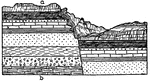
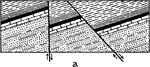
Checkerboard Block Faulting
Diagram showing block faulting of the checkerboard type; peneplanation of the region, and the development…
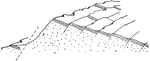
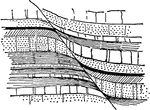
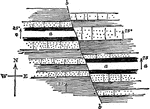
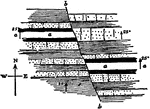
Block Faulting, Sandia Mountains
The mass consists of crystalline rocks, shown by dots, covered by limestones and other sediments, which…
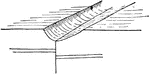
Fault Line Valley
A fault line valley. A fault line, is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the…
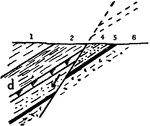
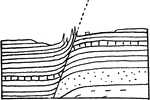
Gravity Fault
A fault is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the fracture has moved with respect…

Gravity Fault
A fault is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the fracture has moved with respect…
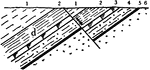
Gravity Fault
A fault is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the fracture has moved with respect…
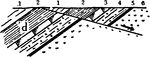
Gravity Fault
A fault is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the fracture has moved with respect…
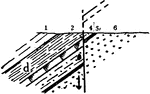
Gravity Fault
A fault is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the fracture has moved with respect…
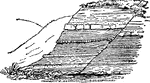
Reverse Fault
A reverse fault is the opposite of a normal fault — the hanging wall moves up relative to the…
Strike Fault
"The two faults of larger throw, by which a single sheet of trap is represented in three ridges, are…
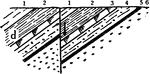
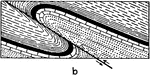
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust with resulting movement of each side…
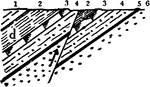
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust with resulting movement of each side…
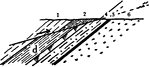
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust with resulting movement of each side…
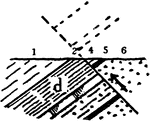
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust with resulting movement of each side…
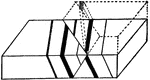
Thrust Fault Diagram
Diagram illustrating the offset of strata produced by vertical slipping along an inclined plane, when…
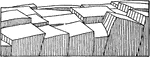
Block Faulting
Diagram illustrating block faulting, and the initial stage in the formation of block mountains.
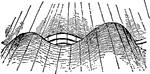
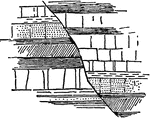
Diagram of Undulating Strata Cut by a Fault
An illustration of undulating strata cut by a fault with alternate throw in opposite directions.
Strata Transversed by a Diminshing Strike Fault
An illustration of a plan of strata transversed by a diminishing strike fault.

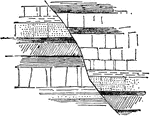
Strata with Fault Line
An illustration of strata bent at a line of fault. In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural:…

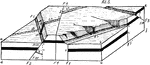
Plan of a Strike Fault
An illustration of the plan of a strike fault. The fault surface is usually near vertical and the footwall…