Clipart tagged: ‘fiber’
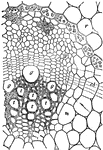
Cambium
"Transverse section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; cb, continuation of cambium between…
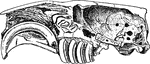
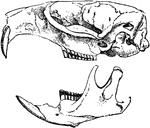
Castor Fiber
"Vertical and Longitudinal section through skull of Castor Fiber, showing the cerebral cavity, the greatly-developed…

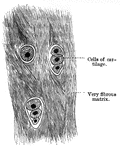
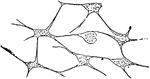
Connective Tissue
"Presently in the production of ordinay connective tissue, fibers of two kinds make their appearance…
Connective Tissue
"Presently in the production of ordinay connective tissue, fibers of two kinds make their appearance…
Connective Tissue
"Connective tissue of sponge." — Encyclopedia BSponge Diver Counting Cardsritannica, 1893
Connective Tissue
"Connective tissue of slug. r, ramified cell; f, flattened cell; v, vesicular cell. The fibers in the…

Cotton
Cotton is a soft fiber that grows around the seeds of the cotton plant. The fiber is often spun into…

Cotton Plant
An illustration of a cotton plant. Cotton is a soft, staple fiber that grows around the seeds of the…

Epiderm Cels
"Epidermo-muscular cells of Hydra m, muscular-fiber processes." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893
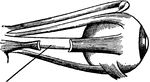
Muscles of the Eyes
"The eye is moved about by six muscles. The back ends of these muscles are attached to the eye sockets.…

Fiber
"Branching fiber, from spiral vessels of Gourd (Cucurbita Pepo)." — Encyclopedia Britanica, 1893
Mustle Fiber
There are two fiber types, slow-twitch muscle, or fast-twitch muscle. Most animals have some combination…
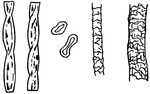
Fibers
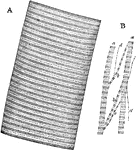
Figure A shows cotton fibers which are smooth on the surface, where as figure B shows woolen fibers…
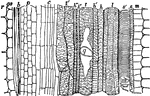
Fibro-vascular Bundle
"Longitudinal section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; s, spiral vessels with fibers which…
Spindle Cell of Involuntary Muscle
"The involuntary muscles consist of ribbon-shaped bands which surround hollow tubes or cavities…
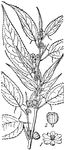
Jute
Jute, also known as Calcutta Hemp, is a fiber obtained from several species of the genus Corchorus of…
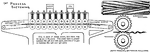
Softening Process in the Manufacturing of Jute
In the manufacturing of jute, the jute fiber must first be softened. The softening machine consists…
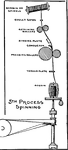
Spinning Process in the Manufacturing of Jute
In the last step of the manufacturing process of the jute plant, the material is taken on bobbins to…

Kapok
A pod of the Kapok (Ceiba pentandra) is a tree in the Malvaceae family of mallows that produces a cotton-like…
Melon Fibers
"Spiral vessels of the Melon, showing the elastic fibers uncoiled, and the vessels overlapping at their…
Muscular Fiber
A. Portion of a medium sized human muscular fiber. B. Separated bundles of fibrils equally magnified.…

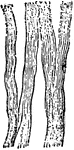
Muscular Fiber
Three muscular fibers running longitudinally, and two bundles of fibers in transverse section, M, from…
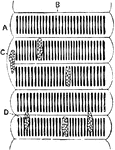
Striped Muscular Fiber of a Beetle
Part of a striped muscle fiber of a water beetle prepared with absolute alcohol. Labels: A, sarcolemma;…
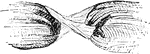
Torn Muscular Fiber
Muscular fiber torn across; the sarcolemma still connecting the two parts of the fiber.
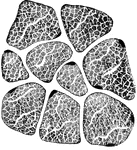
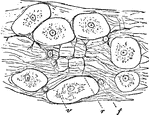
Muscular Fibers of the Human Tongue
Transverse section through muscular fibers of human tongue. The muscle corpuscles are indicated by their…
Portion of a medullated nerve fiber
"The axis cylinder is in the center. On either side is seen the medullary sheath, represented by dark…
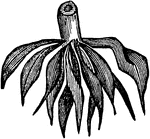
Fasciculated Root
"When the fibers of roots become enlarged by the deposition of starch, they form this variety of root."—Darby,…
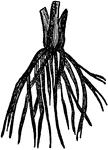
Fibrous Root
"This variety consists of numerous fibers proceeding from the neck of the plant, and may be seen in…
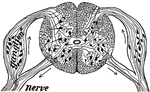
Section of Spinal Cord
"Diagram of a slice across the spinal cord, showing the roots of a spinal nerve to the arm on the left.…
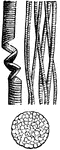
Striped Muscular Fiber
"A Portion of a Striped Muscular Fiber. Highly magnified. A, fiber separating into disks; B, fibrillae;…
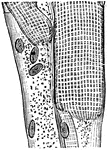
Striped Muscular Fiber
"A Portion of Striped Muscular Fiber, showing Stripes and Nuclei. Highly magnified." — Blaisedell,…
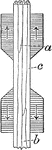
Behavior of Fibers in Tension Test
"Since the strength of the fibers in adhesion is very much less than in tension and compression, adhesion…