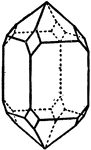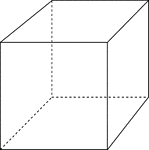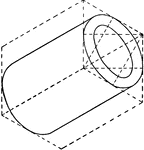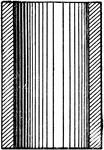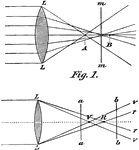
Aberration
"In optics, a deviation in the rays of light when unequally refracted by a lens or reflected…
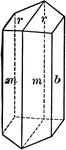
Amphibole
"Monoclinic. Crystals prismatic in habit; the prism faces make angles of 55 and 125 degrees with each…
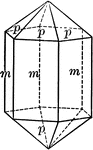
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
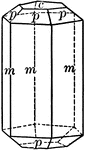
Apatite
"Hexagonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually long prismatic in habit; sometimes short prismatic or tabular.…
Aragonite
"Orthorhombic. Acicular pyramidal; consisting of a prism terminated by a combination of a very steep…
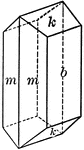
Aragonite
"Orthorhombic. Tabular; consisting of prominent brachypinacoid faces modified by a prism and a low brachydome."…
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
Barite
"Orthohombic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to base; often diamond shaped because of the presence…
Brachy-prism and Macro-pinacoid
"This consists of four faces perpendicular to the vertical axis." -The Encyclopedia Britannica 1910
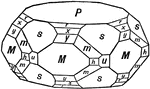
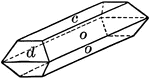
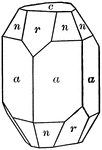
Calcium Phosphate, Apatite
This crystal of Calcium Phosphate, Apatite, represents a complex combination of hexagonal hemihedral…
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
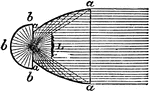
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Combination of a bipyramid and prism
"...a combination of a bipyramid of the first order with a ditetragonal bipyramid and the prism of the…
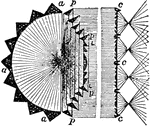
Condensing Light
"Fixed Conensing Light for a Single Sector, 1850.—The holophote Light pLp throws its whole light on…
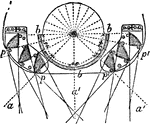
Condensing Octant
"Condensing Octant.—The central fixed apparatus bb with spherical mirror dd throws its rays directly…
Condensing Octant
"Condensing Octant.—The central fixed apparatus bb with spherical mirror dd throws its rays directly…
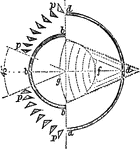
Condensing Quadrant
"Condensing Quadrant.—The fixed apparatus bbb, with spherical mirror behind, throws its rays directly…
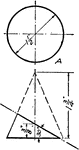
Development Exercise of Cone
Development and top completion exercise problem of the cone by dividing the base into equal parts and…
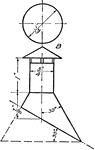
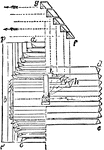
Development Exercise of Flange and Hood Cones
An exercise problem to complete the top and develop, stretched out, image of the flange and hood cones…
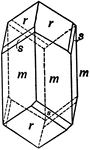
Copper Silicate Showing Rhombohedral Tetartohedrism In the Hexagonal System
This is a crystal of Copper Silicate (Dioptase) with a rhombohedron of the third order, (s), in combination…
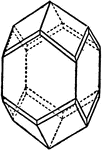
Corundum
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral. Crystals usually prismatic in habit or tapering hexagonal pyramids." —…
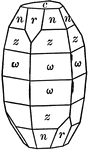
Corundum
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral. Crystals usually prismatic in habit or tapering hexagonal pyramids." —…
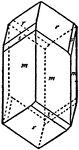
Crystal of Dioptase
"...represents a crystal of dioptase with the fundamental rhombohedron (r) and the hexagonal prism of…
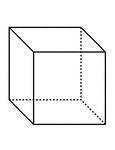
Cube
"A cube is a prism whose faces are ends are squares. All the faces of a cube are equal." —Hallock…
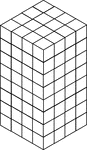
128 Stacked Congruent Cubes
Illustration of 128 congruent cubes stacked so they form a rectangular solid that measures 4 by 4 by…
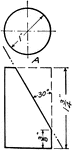
Development Exercise of Cylinder
An exercise problem in creating a development or rolled out surface of a cylinder in a 4" by 5" drawing…
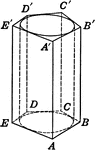
Cylinder Inscribed in Pentagonal Prism
Right circular cylinder inscribed in a pentagonal prism. Or, Pentagonal prism circumscribed about a…
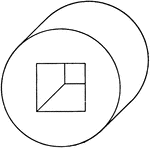
Oblique View Of Hollow Cylinder
Illustration of an oblique view of a hollow cylinder. The portion removed from the center of the cylinder…

Dioptric Holophote
"Perfect Form of Dioptric Holophote for an Oil Flame.—By combining the back prisms ga, hc just described…
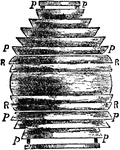
Dioptric Light
"First Application of Total Reflexion to Fixed Lights. In this apparatus Fresnel substituted his totally…
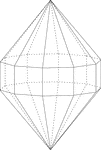
Elongated Decagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated decagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a decagonal bipyramid…
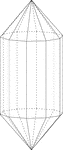
Elongated Decagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated decagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a decagonal bipyramid…
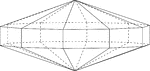
Elongated Decagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated decagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a decagonal bipyramid…
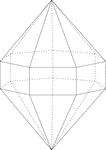
Elongated Heptagonal/Septagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated heptagonal/septagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a heptagonal…
Elongated Heptagonal/Septagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated heptagonal/septagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a heptagonal…
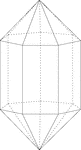
Elongated Heptagonal/Septagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated heptagonal/septagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a heptagonal…
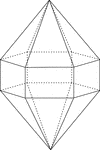
Elongated Hexagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated hexagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a hexagonal bipyramid…
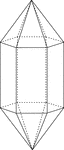
Elongated Hexagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated hexagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a hexagonal bipyramid…
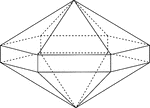
Elongated Hexagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated hexagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a hexagonal bipyramid…
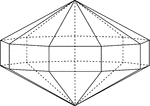
Elongated Nonagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated nonagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a nonagonal bipyramid…
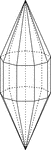
Elongated Nonagonal Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated nonagonal dipyramid that is formed by elongating a nonagonal bipyramid…
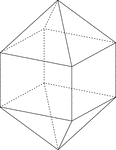
Elongated Square Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated square dipyramid that is formed by elongating a square bipyramid by inserting…
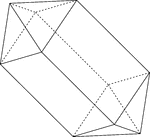
Elongated Square Dipyramid
Illustration of an elongated square dipyramid that is formed by elongating a square bipyramid by inserting…
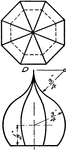
Development Exercise of Dome and True Shape of Hip
A development or rolled out image exercise problem of the dome and finding the true shape of the hip,…
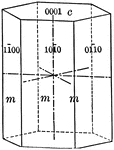
Prism of the first order
"This is a form consisting of six rectangular vertical faces each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
First Right Square Prism
"Science has succeeded in classifying the thousands of known crystals in six systems, to each of which…
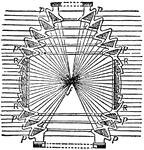
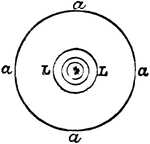
Fresnels Revolving Light
"Fresnel's Revolving Light. —In this form of revolving light the central burner is surrounded by annular…
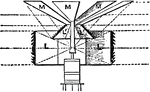
Fresnels Revolving Light
"Fresnel's Revolving Light. —In this form of revolving light the central burner is surrounded by annular…
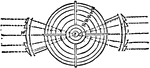
Fresnels Revolving Light
"Fresnel's Revolving Light. —In this form of revolving light the central burner is surrounded by annular…
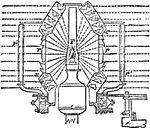
Fresnels Revolving Light
"Fresnel's Revolving Light. —In this form of revolving light the central burner is surrounded by annular…