Electrical Fields
This science ClipArt gallery offers 14 illustrations of forces and fields produced by electric charges on each other and on the environment around them.
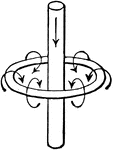
Vertical conductor
"A vertical conductor carrying an electric current, and surrounded by a magnetic line of force, which…
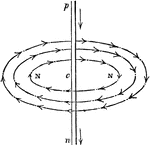
Circular Motion of the [Electric] Fluid
"Thus, if we suppose the conducting wire be placed in a vertical situation, as shown, and p, n, the…
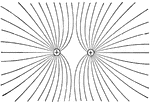
Electricity
This illustration shows the field between two equally and oppositely charged spheres, mapped out by…
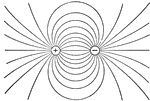
Electricity
This illustration represents the field between two equal positive charges; in this case the lines of…
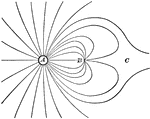
Electricity
This illustration shows the lines of force when a positive charge equal to 4 at A, and a negative charge…
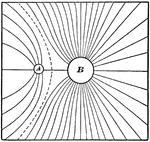
Electricity
This illustration shows the field of force due to a charge 1 at A, and a like charge 4 at B.
Electricity
This illustration shows the field of force between two parallel planes. At the edges its lines of foce…
Electricity
A is a positively charged conductor and B represents the equal and oppsite charge. When the conductor…
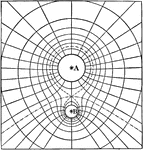
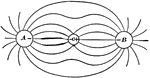
Equipotential
"Equipotential Lines about two similarly electrified spheres, A and B, the quantities of electricity…
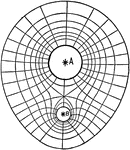
Equipotential Lines
"When a charge is moved from any point to another point in the same equipotential surface, no work is…
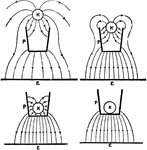
Faraday's Ice Pail Experiment Explanation
"Explamation of Faraday's ice pail experiment." -Hawkins, 1917
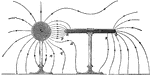
Lines of Force under Induction
"Lines of force of a charged sphere and a conductor under induction. The negative electrification on…
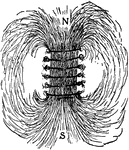
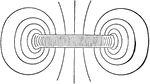
Solenoid
"Coil some No. 12 copper wire throuh holes in a board, as shown, and pass a strong current through it.…
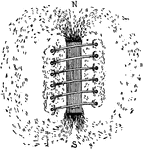
Solenoid with Iron Bar
"Place a strip of shet iron in the solenoid, as shown...Hotice that most of the lines of force are gathered…