!["Bounded by twelve rhomb-shaped faces parallel to the six dodecahedral planes of symetry. the angles between the normals to adjacent faces are 60 degrees...[and] 90 degrees; the indices are {110}" -The Encyclopedia Britannica 1910](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/35500/35528/rhom_35528_mth.gif)
Rhombic Dodecahedron
"Bounded by twelve rhomb-shaped faces parallel to the six dodecahedral planes of symetry. the angles…
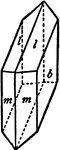
Simple Crystal of Gypsum
"...to be cut in half by this plane (the twinned plane, reference Twinned Crystal of Gypsum) and one…
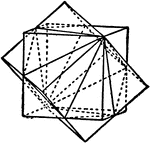
Interpenetrating Twinned Cubes
"Here one cube may be brought into the position of the other by a rotation of 180 degrees about a traid…
!["If the ball approaches the floor under a larger or smaller angle, its rebound will observe the same rule [of reflected motion]." -Comstock 1850](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/35700/35754/reflect2_35754_mth.gif)
Reflected Motion
"If the ball approaches the floor under a larger or smaller angle, its rebound will observe the same…
Inclined Plane
"This power, the most simple of all machines, consists of a hard, smooth, plane, inclined to the horizon…
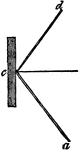
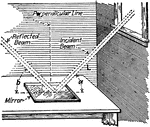
Reflection of Light
"The ray a, c, is the ray of incidence, and that from c, to d, is the ray or reflection. The angles…
Plane Mirror
"Suppose the mirror, a b, to be placed on the side of a room, and a lamp to be set in antoher room,…
!["This will be understood [here] where the ray of light A B, proceeding from the eye, falls perpendicularly on the plane mirror B D. will be reflected back in the same line; but the ray C D coming from the feet, which falls obliquely on the mirror, will be reflected back under the same angle in the line D A; and since we see objects in the direction of the reflected rays, and the image appears at the same distance behind the mirror that is object is before it, we must continue the line A D to the feet, E, and for the same reason, the rays A B, from the eye, must be prolonged to F, as far behind the mirror as the line E extends, where the whole image will be represented." -Comstock 1850](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/35800/35843/mirror3_35843_mth.gif)
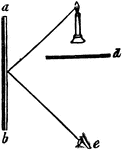
Mirror Half the Length of the Object
"This will be understood [here] where the ray of light A B, proceeding from the eye, falls perpendicularly…
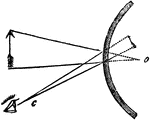
Convex Mirror
"...as the arrow is moved backwards, the angle at c, must be diminished, because the rays flowing from…
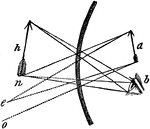
Object Within the Focus in a Concave Mirror
"...let us suppose the object a, to be placed before the mirror, and nearer to it than the principal…
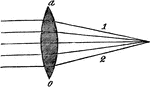
Diverging Rays from a Double Convex Lens
"If diverging rays fall on the surface of the same lens, they will, by refraction, be rendered less…
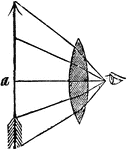
Visual Angle
"Suppose the object a, appears to the naked eye of the length repreesnted in the drawing. Now, as the…
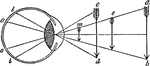
Angle of Vision
"The angle under which the rays of light, coming from the extremities of an object, cross each other…
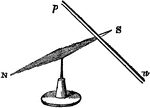
Wire at Right Angle to the Uniting Wire
"Direction of the needle when placed at a right angle to the uniting wire." -Comstock 1850

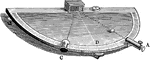
Torsional Pendulum
"Firmly fasten one end of a piece of spring-brass wire, about No. 27 and about 1 m. long so that the…
Law of Reflected Motion
"The angle, ABD, included between the direction of the moving body before it strikes the reflecting…

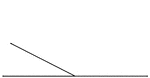
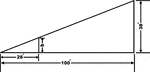
Inclined Plane
"An inclined plane is a smooth, hard, inflexible surface, inclined so as to make an oblique angle with…
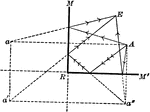
Multiple Images in a Plane Mirror
"By placing two plane mirrors facing each other, we may produce an indefinite series of images of an…
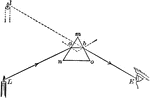
Prism
"A prism is a transparent body with two refraction surfaces that lie in intersecting planes. The angle…
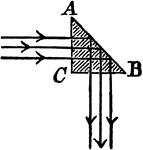
Cathetal Prism
"Cathetal prisms readily yield the phenomena of total reflection as shown, and are often used when light…
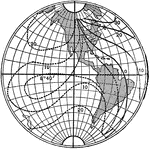
Isogonic Lines of Earth
"The magnetic poles of the earth do notc oincide with its geographical poles and, condequently, in some…
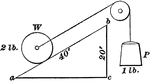
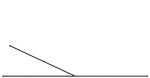
Inclined Plane with the Force Acting Parallel to the Plane
"An inclined plane is a slope, or flat surface, making an angle with a horizontal line...the force acts…
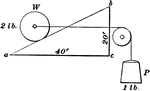
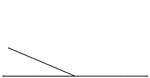
Inclined Plane with the Force Acting Parallel to the Base
"An inclined plane is a slope, or flat surface, making an angle with a horizontal line...the force acts…
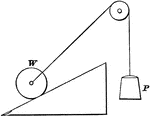
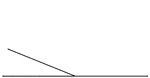
Inclined Plane with Force at an Angle to Plane and Base
"An inclined plane is a slope, or a flat surface, making an angle with a horizontal line...the force…

Sulphur
"An allotrope of sulphur, when heated to 115 degrees Celcius, will cool to be yellowish-brown, needle-shaped…
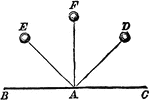
Reflected Motion
"... if a ball be thrown from F against the surface B C so as to strike it perpendicularly at A, it…
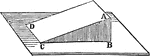
Inclined Plane
"One of the primary simple mechanical powers. The plane's surface is inclined to the horizon at any…
Thermometer
"A bulb of liquid is placed in the base of the glass graduated tube. As temperature increases, the volume…
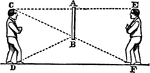
Angle of Incidence and Reflection
"Mirror A/B is only half of person C's height. C is able to view his entire body through such a small…