Avocet
A wader bird native to warm and hot climates. Commonly 15 to 18 inches tall and has a chestnut color…
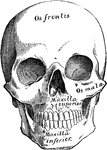
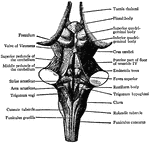
Mouth
"The mouth, nose and pharynx, with the commencement of the gullet and larynx, as exposed by a section,…
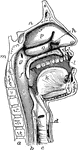
Proboscis
"Diagrammatic vertical section of the head and proboscis of a mosquito. l, labium bent as when the other…
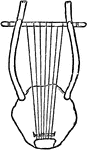
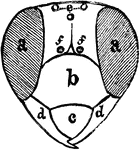
Chelys
"Chelys, from a vase in the British Museum, where also are fragments of such an instrument, the back…

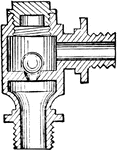
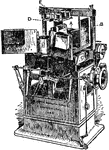
Screw-Cutting
"A self-acting screw-cutting lathe with double-geared headstock, of a type now well established, the…
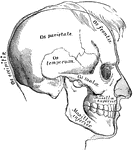
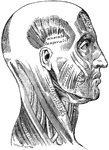
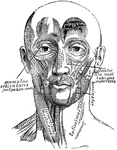
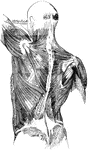
Lower Extremity
The lower extremity of the human body. 1: Head of femur; 2: Femur; 3: Patella; 4: Tibia; 5: Fibula;…

Chaeronycteris Mexicana
"Head of Chaeronycteris Mexicana, showing fibrillated tongue." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903

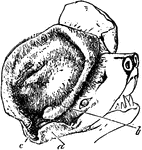
Lophiomys Imhausi
"This very extraordinary species from north-east Africa differs from all other rodents in the peculiar…

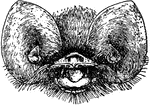
Antelope Head
"Head of antelope (Gazella granti), showing horns." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903

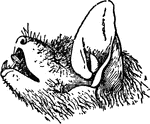
Manatee Face
"Front view of head of American Manatee, showing the eyes, nostrils, and mouth with the lobes of the…

Manatee Face
"Front view of head of American Manatee, showing the eyes, nostrils, and mouth with the lip contracted."…

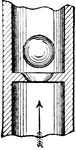
Micrometer
"The original Merz micrometer of the Cape Observatory, made on Fraunhofer's model. S is the head of…
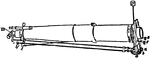
Heliometer
"No part of the equatorial mounting is shown in the figure, as it resembles every respect that usual…
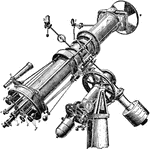
Micrometer
"The circles for position angle and declination are read by micrometer microscopes illuminated by the…

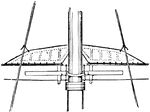
Balloon Jib
A triangular sail made of light canvas, used only in light winds and on yachts, set between the foretop…
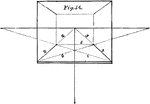
Parallel Perspective
The perspective shown in this plate is parallel perspective; and the subject here intended to be represented…
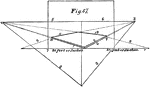
Angular Perspective
The perspective in this plate is "angular perspective," and the figure it represents is a flat square…
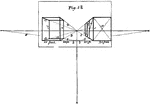
Parallel Perspective
Two upright oblong figures are here represented in parallel perspective. They may be imagined to resemble…
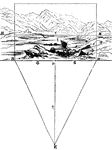
Distance
"A landscape is supposed to be viewed from the spot marked E; and that the spectator is desirous of…

Buffalo Gnat
They are rather undersized, chunky flies, dark in color, with the thorax well developed and somewhat…