Laurel Hill
"Advance of General Rosecrans's division through the forests of Laurel Hill to attack the Confederate…

Battle of Cross Keys
"The Battle of Cross Keys- opening of the fight- the federal troops, under General Fremont, advancing…

Colonel E. E. Cross
"Colonel Cross, born in Lancaster, N. H., April 22nd, 1832, died near Gettysburg, Pa., July 22nd, 1863.…

Storming of Fort Donelson
"Storming of Fort Donelson- decisive bayonet charge of the Iowa Second Regiment on the Confederate intrenchments…

Munson's Hill
"Skirmishing between the pickets of the two armies near Munson's Hill- the hill in the distance. Munson's…

Battle of Pea Ridge
"Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., fought March 6th, 7th and 8th, 1862, between the Federal forces, 13,000…

Fox Hound
"A cross between an old english hound and the greyhound. It is from twenty-two inches to two feet in…

American Cross Fox
"The size is that of the common fox, the fur exceedingly long, soft, and rich; and, although presenting…

Crossing of Shenandoah River
"Colonel Pilson's Battery shelling the rear guard of the Confederate General Jackson's Army, at the…

Battle at Willis Church
"Battle at Willis Church, Monday, June 30th, 1862- the Federal forces, under General Heintzelman, engaged…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Cross Keys
"Battle of Cross Keys, Sunday June 8th, 1862- centre and front of the Federal army in the engagement.…

Commencement of Bull Run
"The Confederate forces under General Jackson advancing upon the Rapphannock Station at the river. Federal…

General Fitzjohn Porter
"General Porter, born at Portsmouth, N. H., June 13th, 1822, was graduated from the United States Military…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Jack and Jill
Jack and Jill went up the hill to fetch a pail of water. Jack fell down and broke his crown, and Jill…

Jack and Jill
Jack and Jill went up the hill to fetch a pail of water. Jack fell down and broke his crown, and Jill…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Md. Burnside's division carrying the bridge over the Antietam Creek and storming…

Army of the Potomac
"Advance of the Army of the Potomac. Occupation of Winchester, VA., and the abandoned Confederate Fortifications,…

The Forlorn Hope
"'The Forlorn Hope.' Volunteers storming party, consisting of portions of the Seventh Michigan and Nineteenth…

Federal Hill
"Federal Hill, Baltimore, taken from the North side basin, occupied by the Federal Troops."— Frank…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Burnside's Division, left wing- brilliant and decisive bayonet charge of Hawkins's…

Confederate Cavalry
"Confederate cavalry driving stragglers and skulkers back to their duty at the Battle of Antietam. One…

Pippin Hill
"As I was going up Pippin Hill, Pippin Hill was dirty. There I met a pretty miss, And she dropped me…

Battle of Baker's Creek
"Battle of Baker's Creek, May 16th, 1862- Defeat of the Confederates under Pemberton, by General Grant.…

General Gouverneur K. Warren
"General Warren, born in Cold Spring, N. Y., January 8th, 1830, died in Newport, R. I., August 8th,…

General John James Peck
"General Peck, born at Manlius, N. Y., January 4th, 1821, died at Syracuse, n. Y., April 28th, 1978,…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. The decisive charge of General Negley's division across the river- the…

Siege of Vicksburg
"Siege of Vicksburg- the fight in the crater of Fort Hill after the explosion, June 27th, 1863. Our…

Battle of Gettysburg
"Battle of Gettysburg, Cemetery Hill during the attack of the Confederates, Thursday evening, July 2nd,…

Battle of Chancellorsville
"Battle of Chancellorsville, Va. Attack on General Sedgwick's Corps. on Monday, May 4th, 1863, at 5…

Siege of Vicksburg
"Siege of Vicksburg. Life in the trenches- bivouac of Leggett's Brigade- McPherson's Corps at the White…

Battle of Gettysburg
"Battle of Gettysburg- charge of the Confederates on Cemetery Hill, Thursday evening, July 2nd, 1863.…

Attack on Confederate Works
"Siege of Vicksburg, attack on the Confederate Works, May 22nd, 1863. Our sketch represents the terrible…

Siege of Vicksburg
"Siege of Vicksburg-the Twenty-third Indiana and Forty-fifth Illinois Regiments, Leggett's Brigade,…

Confederate Batteries
"Fredericksburg, Va., and the Confederate batteries and pickets, as seen from Falmouth Heights, headquarters…

Battle of Gettysburg
"Battle of Gettysburg, Thursday evening, July 2nd, 1863, as seen from Rocky Hill, on Meade's left. Our…

Bogue Island
"The Federal siege works on Bogue Island, N. C., erected for the reduction of Fort Macon. Our sketch…

Loudon Heights
"View from Loudon Heights, Va., showing Harper's Ferry, Maryland Heights, Bolivar, etc. Harper's Ferry,…

Bucktail Recruit
"Recruiting in Philadelphia, Pa., for the Bucktail Pennsylvania Regiment, August, 1862. This famous…

General Cuvier Grover
"General Grover, born in Bethel, Me., July 24th, 1829, died in Atlantic City, N. J., June 6th, 1885,…

Battle of Chickamauga
"Battle of Chickamauga, Ga., September 19th-20th, 1863, between Generals Rosecrans and Bragg. Our sketch…

Falling Waters
"Gallant charge of the Sixth Michigan cavalry over the enemy's breastworks, near falling Waters, Md.,…

General Thomas J. Jackson
"General Stonewall Jackson, born in Clarkesburg, W. Va., January 21st, 1824, died at Chancellorsville,…

Hooker's Battle
"The war in Tennessee. Hooker's Battle above the clouds, and capture of the Confederate position on…

Fort Stevens
"The operations near Washington, scene of the fight in front of Fort Stevens, July 12th-13th, 1864.…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana. General Banks's army, in the advance on Shreveport, crossing Cane River, March…

Sherman's Campaign
"Sherman's Campaign in Georgia- the attack of the Fourteenth, Sixteenth and Twentieth Army Corps on…

Sheridan's Great Battle
"The war in Virginia- Sheridan's Great Battle with J. E. B. Stuart at Yellow Tavern, May 11th, 1864-…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee. Capture of Mission Ridge, near Rossville, by General Thomas, November 25th, 1863.…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11800/11856/petersburg_11856_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…

Jackson Hill
"Sheridan's campaign in the valley of the Shenandoah- view of the front from the Federal lines on Jackson…

General Sheridan
"Major General Sheridan riding along the lines after the Battle of Fisher's Hills, Va., September 22nd,…

Battlefield of Gettysburg
"The battlefield of Gettysburg- breastworks, Culp's Hill- Gettysburg in the distance."— Frank…

General William Mahone
"General Mahone, born in Southampton County, Va., December 1st, 1826; died at Washington, D. C., October…
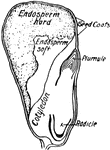
Kernel of Corn
Cross-section of a kernel of corn. Food is stored in the cotyledon and in the endosperm which surrounds…
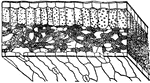
Cross-section of a leaf
Cross section of a leaf, showing the breathing pores and intercellular spaces. The small dots are grains…