Sarcophagus of Scipio
"Sarcophagus, plural Sarcophagi, is a kind of stone used among the Greeks for making coffins, and so…

Hooded Seal
"The Seal, of the family Phocidæ, or seal tribe, are, of all four-limbed mammiferous animals,…

Giant Sloth
"Sloth is the popular name for any individual of the Edentate group Tardigrada, from their slow and…

Sphinx
"Sphinx is a Greek word signifying 'strangler,' applied to certain symbolical forms of Egyptian origin,…

Spider Monkey
"Spider Monkey is a general name applied to many species of platyrhine or New World monkeys, distinguished…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured] Lesser Sand-star (Ophiura albida)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16266/starfish1_16266_mth.gif)
Lesser Sand-Star Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Common Starfish, reproducing rays"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16277/starfish2_16277_mth.gif)
Common Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Common Starfish (Asterias rubens)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16278/starfish3_16278_mth.gif)
Common Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Eyed Cribella (Cribella oculata)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16280/starfish4_16280_mth.gif)
Eyed Cribella Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
!["Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the Atlantic coasts. The body is more or less star shaped, and consists of a central portion, or disk, surrounded by five or more lobes, or arms, radiating from the body and containing prolongations of the viscera. The mouth is situated in the center of the lower surface of the body, and the anus is either absent or on the upper surface. Locomotion is effected by means of peculiar tube-like processes, which are protruded from the under surface of the arms. They possess in a high degree the power of reproducing lost members and abound in all seas. [Pictured]Gibbous Starlet (Asterina gibbosa)"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16200/16282/starfish5_16282_mth.gif)
Lesser Sand-star Starfish
"Starfish is a popular name for any individual of the family Asteridæ, a familiar object on the…
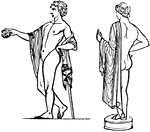
Chlamys
"A scarf, denoted an article of the amictus, or outer raiment of the Greeks. It was for the most part…

Emissarium
"An artificial channel formed to carry off any stagnany body of water, like the sluices in modern use.…

Cudgel Game
"Here is a new game, which is causing a great deal of amusement at social gatherings in Europe. Two…

Common Swift
"The Swift, like swallows in many respects, their structure is almost entirely different, and some naturalists…

Swordbill
"Swordbill is a popular name for any individual of the humming bird genus, Docimastes. The bill which…
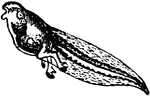
Tadpole
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…

Tadpole
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…
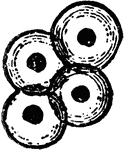
Frog Eggs
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…

Frog Egg
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] A single segment or proglottis magnified; 1, generating pore; 2, water vessels; 3, dendritic ovary."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16500/16595/tapeworm2_16595_mth.gif)
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] Head of tænia solium (enlarged)."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16500/16599/tapeworm3_16599_mth.gif)
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…
!["The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length is from 5 to 15 yards, and its breadth from two lines at the narrowest part to four or five at the other or broader extremity. At the narrow end is the head, which is terminated anteriorly by a central rostellum, surrounded by a crown of small recurved hooks, and behind them four suctorial depressions; then follow an immense number of segments, each full of microscopic ova. The segments are capable of being detached when mature, and reproducing the parasite. There is no mouth; but nutrition appears to take place through the tissues of the animal, as algæ derive nourishment from the sea water in which they float. The digestive system consists of two tubes or lateral canals, extending from the anterior to the posterior end of the body, and a transverse canal at the summit of each joint. [Pictured] A, ovum with contained embryo, B, Cystericus longicollis."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16600/16600/tapeworm4_16600_mth.gif)
Tapeworm
"The Tapeworm is an intestinal worm, Tænia solium, in form somewhat resembling tape. Its length…

Tarantula
"The Tarantula is a large spider, with a body about an inch in length; its bite was formerly supposed…
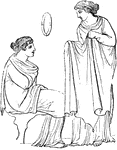
Peplus
"The peplus was a shawl which commonly formed part of the dress of females. It was often fastened…

Halteres
"Halteres were certain masses of stone or metal, which were used in the gymnastic exercises of the Greeks…
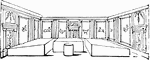
Banqueting room
"The Roman people reclined at their meals. On each couch there were commonly three persons. They lay…
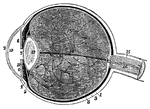
Human Eye
1, the sclerotic thicker behind than in front; 2, the cornea; 3, the choriod; 6, the iris; 7, the pupil;…
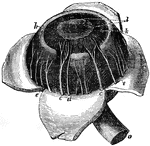
Human Eye
c, ciliary nerves going to be distributed in iris; d, smaller ciliary nerve; e, veins known as vasa…
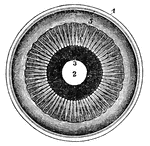
Human Eye
The iris and adjacent structures seen from behind. 1, the divided edge of the three coats, the choroid…

Peplum
"An outer garment, strictly worn by females, and thus corresponding to the himation or pallium, the…
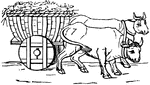
Plaustrum
"A cart or wagon. It had commonly two wheels, but sometimes four, and it was then called the plaustrum…
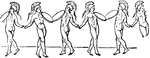
Salatio
"Dancing. The dancing of the Greeks as well as of the Romans had very little in common with the exercise…

Salatio
"Dancing. The dancing of the Greeks as well as of the Romans had very little in common with the exercise…
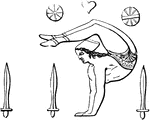
Salatio
"Dancing. The dancing of the Greeks as well as of the Romans had very little in common with the exercise…
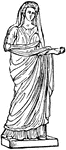
Stola
"A female dress worn over the tunic; it came as low as the ankles or feet, and was fastened round the…
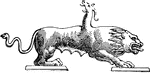
Chimera
A fire breathing monster, the fore part of whose body, according to the Iliad, was that of a lion, the…

Change Direction Signal
"The hand on the side toward which the change of direction is to be made is carried across the body…
Parade Rest
"Carry the right foot 6 inches straight to the rear, left knee slightly bent; clasp the hands, without…
Present Arms
"With the right hand carry the piece in front of the center of the body, barrel to the rear and vertical,…
Port Arms
"With the right hand raise and throw the piece diagonally across the body, grasp it smartly with both…
Parade Rest with Rifle
"Carry the right foot 6 inches straight to the rear, left knee slightly bent; carry the muzzle in front…

American Dipper
A bird that spends most of its time in the water. It has a thick body; very short tail of 12 rectrices…
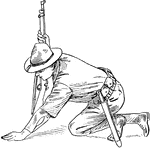
Lie Down
"Carry back the left foot and lie flat on the belly, inclining the body about 35 degree to the right."…

Lie Down
"Carry back the left foot and lie flat on the belly, inclining the body about 35 degree to the right."…

Bayonet Guard
"At the second command sake the position of guard; at the same time throw the rifle smartly to the front,…

Low Parry
"Carry the point of the bayonet down until it is at the height of the knee, moving the point of the…

Low Parry
"These parries are rarely used, as an attack below the waist leaves the head and body exposed." —…

Left-Handed Rifle
"As additional instruction, the men may be permitted to wield the rifle left handed, that is on the…
Egg
A body formed in the females of birds, and some other animals, from which their young is produced.