
Non-Vocal Shut Throat Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Throat Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
![Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics of certain central-aperture consonants with the wide or expanded quality of vowels, but differing from vowels in not having a fixed configuration. ...in representing glides the peculiarities of consonants and vowels are blended: the accented fingers, by being straightened, contribute a consonant characteristic; while the second phalanx of the thumb, by being held at an angle to the plane of the palm, imparts to the glide positions the wide, without giving them the firm, quality of vowel positions. <p> Breath-Glide - A transitional aspiration, of organic quality corresponding to that of the adjoining elements [a soft effect of the Consonants, back primary; top primary; Point primary; Lip primary; etc.]. Although this glide has no fixed abiding place, and is of a somewhat variable organic formation, in its effect it is very closely allied to the Throat consonant aspirate, and is therefore represented with a posterior position of the palm and a separation of the index and center fingers, which are characteristic features of Throat positions. This is the only Non-Vocal glide, and hence is the only one in the representation of which the voice phalanx is unaccented.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/65900/65914/65914_glide_breath_mth.gif)
Breath-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
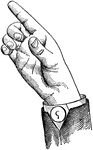
Back-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
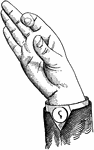
Back Mixed-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Normal Aperture Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
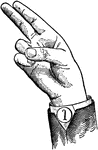
Normal Aperture Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
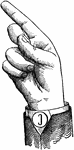
Normal Aperture Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
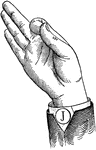
Normal Aperture Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
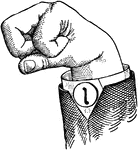
Normal Aperture Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
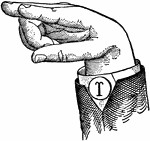
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
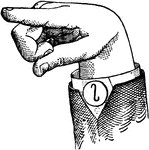
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
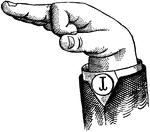
Normal Aperture Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
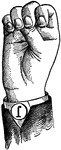
Normal Aperture Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
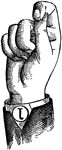
Normal Aperture Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
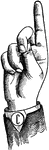
Normal Aperture Front Primary Wide Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Normal Aperture Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
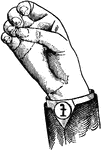
Round Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
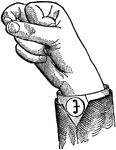
Round Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
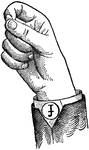
Round Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
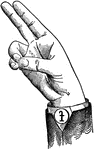
Round Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
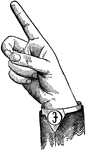
Round Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Mixed Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
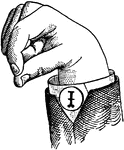
Round Mixed Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
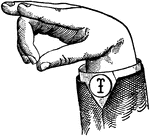
Round Mixed Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
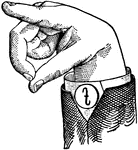
Round Mixed Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
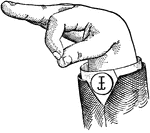
Round Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
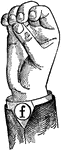
Round Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
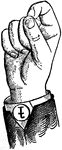
Round Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
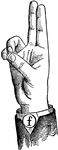
Round Front Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
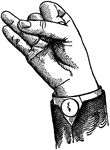
Indicated High Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
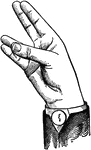
Indicated High Wide Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
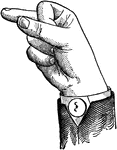
Indicated Mid Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
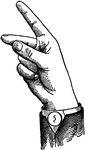
Indicated Mid Wide Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
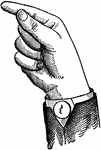
Indicated Low Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
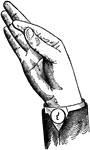
Indicated Low Wide Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Rahab and the Spies
"And the king of Jericho sent unto Rahab, saying, Bring forth the men that are come to thee, which are…

Falling of the Walls of Jericho
"And it came to pass on the seventh day, that they rose early at the dawning of the day, and compassed…
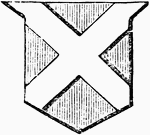
Saltier Ordinary
5 Then went Samson down, and his father and his mother, to Timnath, and came to the vineyards of Timnath:…

Samson Slaying the Lion
"Then went Samson down, and his father and his mother, to Timnah, and came to the vineyards of Timnah:…

Ruth Gleaning in the Fields of Boaz
"Then said Boaz unto his servant that was set over the reapers, Whose damsel is this?And the servant…
Many-flowered Darnel
The Many-flowered Darnel (Lolium multiflorum) is the most showy species of rye grass cultvated. Three…
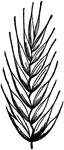
Many-flowered Darnel
The Many-flowered Darnel (Lolium multiflorum) is the most showy species of rye grass cultvated. Three…
Wild Oat Grass
Wild Oat Grass (Danthonia spicata), also referred to as White Top grass, and Old Fog grass, is common…

Wild Oat Grass
Wild Oat Grass (Danthonia spicata), also referred to as White Top grass, and Old Fog grass, is common…
Wild Oat Grass
Wild Oat Grass (Danthonia spicata), also referred to as White Top grass, and Old Fog grass, is common…
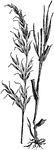
Tall Meadow Oat Grass
Tall Meadow Oat Grass (Arrhenatherum avenaceum), or Tall Oat Grass is the avena elatior of Linnaeus.…
Tall Meadow Oat Grass
Tall Meadow Oat Grass (Arrhenatherum avenaceum), or Tall Oat Grass is the avena elatior of Linnaeus.…
Sweet-scented Vernal Grass
Sweet-scented Vernal Grass (Anthoxanthum odoratum) has three-flowered spreading spikelets. The lateral…
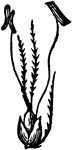
Sweet-scented Vernal Grass
Sweet-scented Vernal Grass (Anthoxanthum odoratum) has three-flowered spreading spikelets. The lateral…