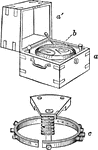
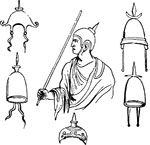
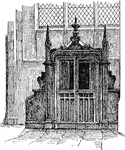
Chrismatory
A receptacle for the chrism, or holy oil, used in the services or the Roman Catholic and Eastern Churches.

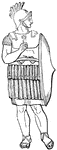
Roman augur
"Represents a Roman augur, with his litmus or divining staff, observing the signs in the heavens." —…
Roman Clypeus
"The following cut represents a Roman clypeus, from the column of Trajan. The projection in the centre…
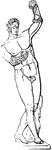
Boxer with cestus
"The cestus was used by boxers from the earliest times. It consisted of thongs of raw ox-hide, or of…

Syrinx
"Syrinx, the Pan's pipe, or Pandean pipe, was the appropriate musical instrument of the Arcadian and…
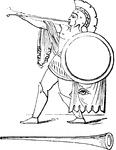
Roman trumpet
"There appears to have been no essential difference in form between Greek and Roman or Tyrrhenian trumpets.…

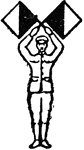
Ancilia
"According to the ancient authorities, it was made of bronze, and its form was oval, but with the two…

Tunica
"Tunica, an under-garment. Roman. The Tunica of the Romans, like the Greek chiton, was a woollen under…

Vestales
"Vestaes, the virgin priestesses of Vesta, who ministered in her temple and watched the eternal fire.…

Umbraculum
"Umbraculum, Umbella, a parasol, was used by Greek and Roman ladies as a protection against the sun.…
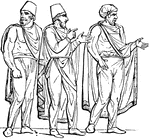
Sagum
"The sagum was open in the front, and usually fastened across the shoulders by a clasp. The form of…

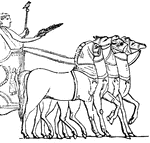
Caesar in England
"All histories of England commence with the invasion of Julius Caesar, the earliest event in that quarter…

Guy Fawkes and his associates
"One of the most extraordinary events in the history of England is that commonly known by the name of…
Pendulum
"A pendulum has a strong tendency to maintain its plane of oscillation, a fact that has been used in…

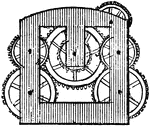
Escapement
"A crank which regulates the motion of the chief or escapement wheel of a train of clock-work worked…

Aneroid Barometer
"This is an instrument shaped something like a small clock, and the barometric pressure is read by means…

German Street Corner
"Each is as big around as a hogshead, and about fifteen feet high; it is covered with printed manner,…
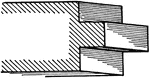
Raised Fillet
A roman moulding, called Raised Fillet. Its projection is generally made equal to its height.…
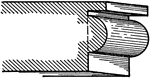
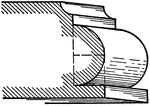
Bead
A roman moulding, called a Bead. It is a molding consisting of a semi-circle on a flat surface.…
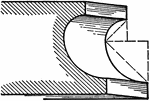
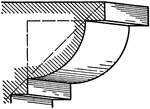
Scotia
A roman moulding, called a Scotia. It consists of two quarter circles one of which has a radius…
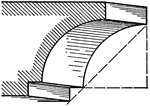
Cavetto
A roman moulding, called a Cavetto. It consists of a quarter circle with a sunk fillet below.…
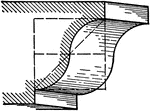
Cyma Recta
A roman moulding, called a Cyma Recta. It is a moulding of double curvature and two fillets.…
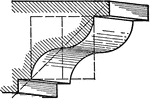
Cyma Reversa
A roman moulding, called a Cyma Reversa. This like the cyma recta, is composed of two quarter…