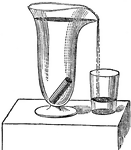
Clipart tagged: ‘Archimedes’
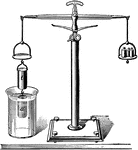
Archimedes Principle
"From on pan suspend a hollow cylinder of metal t, and below that a solid cylinder a of the same size…
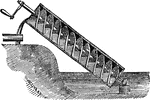
Archimedes Screw
"A machine for raising water, said to have been invented by Archimedes, during his stay in Egypt for…
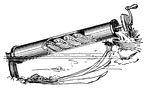
Archimedes' Screw
A machine used for lifting water, thought to have been invented by Archimedes in egypt for draining…
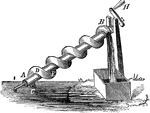
Archimedes' Screw
"Invented to raise water. A hollow tube wound spirally around a solid cylinder. As the cylinder is turned,…

Archimedes' Water Screw
"It consists of a tube, made of lead, or strong leather, coiled round a cylinder of wood or iron, as…
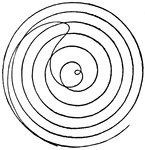
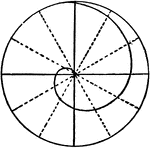
Fermat's Spiral
Also called a parabolic spiral, it is a type of Archimedean Spiral. A spiral is defined as "a plane…
Archimedean Spiral
Illustration of a spiral named after the 3rd century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes.
Hyperbolic Spiral
Illustration of a hyperbolic spiral, also called a reciprocal spiral, it is a transcendental plane curve.…