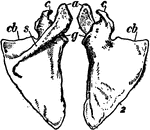
Shoulder blade
"The Scapula, or shoulder blade, is one of the two bones, the other being the clavicle, which form the…
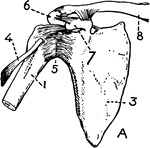
Shoulder bones and ligaments
"Shoulder bones and ligaments. 1. Humerus, 3. Scapula, 4. Tendon of biceps 5. Capsular ligament 6. Acromion…
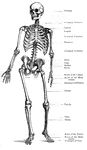
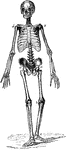
The Human Skeleton
The Human Skeleton. Labels: a, parietal bone; b, frontal; c, cervical vertebrae; d, sternum; e, lumbar…
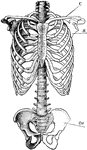
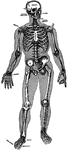
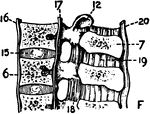
Skeletal Trunk
"The skeleton of the trunk and the limb arches seen from the front. C, clavicle; S, scapula; Oc, innominate…
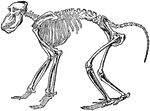
Chacma Baboon Skeleton
"The skeleton, more especially in the higher forms, is in the main similar to that of man, so that only…
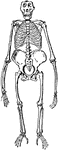
Front View of Gorilla Skeleton
"The greatest absolute length of the fore—limb occurs in the gorilla and the orangutan. The humerus…
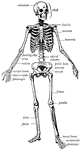
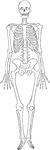
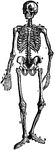
Human skeleton
"The human body, like a great building, has a framework which gives the body its shape and provides…
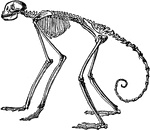
Side View of Skeleton of South American Spider Monkey
"In the other forms the number (vertebrae) varies between twenty and thirty three, the latter being…
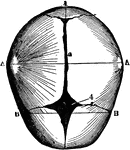
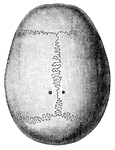
Human Skull at Birth
The skull at birth, superior suerface. The cranial bones of the infant at birth are not fullyformed…
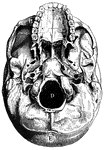
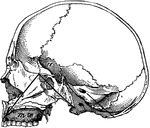
Base of skull
"A, Palate process of upper jawbone; B, zygoma, forming zygomatic arch; C, condyle, for forming articulation…
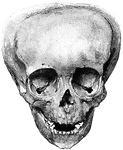
Deformed skull
"Showing how the Bones of the Skull may be artificially deformed by "head-binding." From the photograph…
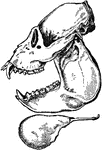
Side View of Howler Monkey
A side view of the howler monkey skull. The monkey have four sharp canines, long teeth on skull, on…
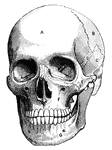
Human skull
"A, frontal bone; B, parietal bone; C, temporal bone; D, sphenoid bone; E, malar bone; F, upper jawbone;…
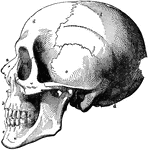
Human Skull
The skull. Labels: a, nasal bone; b, superior maxillary; c, inferior maxillary; d, occipital; e, temporal;…
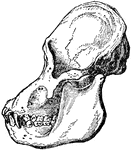
Adult Male Orangutan Skull Viewed from Side
An illustration of an adult male orangutan viewed from the side. The orbit part of the skull is more…
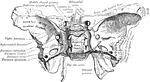
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
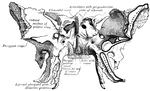
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
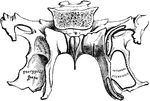
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
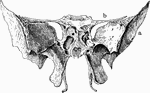
Sphenoid Bone of the Human Skull
Sphenoid bone, situated the anterior part of the base of the skull, articulating with all the other…
Spinal column
"The spine or backbone, serves as a support for the whole body. It is made up of a number of…
Human Spinal Column
Side view of spinal column, without sacrum and coccyx. Labels: 1 to 7, cervical vertebrae; 8 to 19,…
Spine
"The spine, sawn in two lengthwise, showing the spinal canal and the holes between the vertebrae, where…

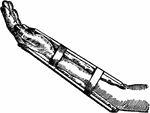
Splint
"No one but a good surgeon is able to set a broken bone successfully. However, if a person with a fracture…
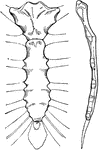
Human Sternum Bone
Sternum, front and side view. The sternum, or breast bone, is a flat narrow bone, situated in the median…
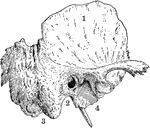
Temporal Bone of the Human Skull
Temporal bone of the human skull. The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull.…
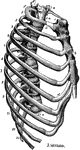
Human Thorax (Chest)
Thorax. The thorax, or chest, is an elongated conical-shaped cage, formed by the sternum and costal…
Tibia and Fibula
"The leg consists, like the forearm, of two bones. The larger, a strong, three-sided bone with…
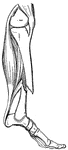
Broken Tibia
"When a bone is broken, blood trickles out between the injured parts, and afterwards gives place to…
Ulna and Radius
"The ulna, or elbow bone, is the larger of these two bones. It is joined to the humerus by…
The Human Ulna and Radius
The Ulna and Radius. Labels: 1, radius; 2, ulna; o, olecranon process, on the anterior surface of which…
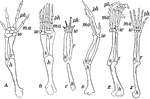
Forearms of vertebrates
"Fore limbs of vertebrates showing similarity of structure. A, salamander; B, turtle;…

Human Vomer Nasal Bone
Vomer bone, a single bone placed at the back part of the nasal cavity, and forms part of the septum…
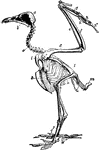
Vulture Skeleton
"Skeleton of Egyptian Vulture. (Neophron percnopterus), to show bones of bird. a, post-orbital process;…
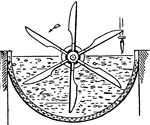
Wash Box for Removing Lime
This illustration shows a wash box used for removing lime from materials used in glue manufacturing.
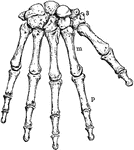
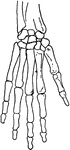
The Human Wrist and Hand Bones
Bones of the Wrist and Hand. Labels: m, metacarpal bones; p, phalanges; 3, bones of wrist.