Clipart tagged: ‘Discharging’
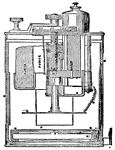
Absolute Electrometer
"Thomson's absolute electrometer is an adaptation of the attracted disc principle for absolute determinations.…

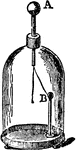
Bennets Electroscope
"The gold leaves are gummed on the two sides of a flat piece of metal carried by a stout stem, which…
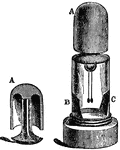
Cavallos Electroscope
"Cavallo's electroscope embodies the double pendulum principle. It consists of two fine silver wires…
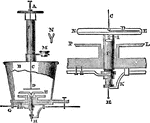
Dellman's Electrometer
"D is a needle, formed of light silver wire, suspended by a fine glass fiber, from a torsion head A.…

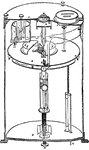
Disc Electrometer
"C is an insulated disc, over which is suspended another disc, hung from the arm of a balance, and connected…
Henleys Electrometer
"The electrometer of Henley, sometimes called Henley's quadrant Henley electrometer, may be taken as…
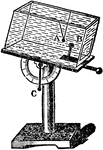
Sine Electrometer
"The sine electrometer of August, is a modification of the single pendulum electroscope, analogous in…