Clipart tagged: ‘Electrometer’
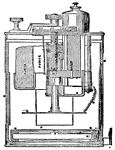
Absolute Electrometer
"Thomson's absolute electrometer is an adaptation of the attracted disc principle for absolute determinations.…
!["One of the best-known instruments of this [electrometer] class is Coulomb's torsion-balance, which consists essentially of gilt ball, i, carried at the end of a horizontal shellac needle that is suspended by a fine silver wire from the top of a tube that rises from the cover of the enclosing glass cylinder. A vertical insulating rod passing through the cover carries a handle, a, and a gilt ball, e, at its ends." -Avery 1895](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36000/36071/torsion_bal_36071_mth.gif)
Coulomb's Torsion-Balance
"One of the best-known instruments of this [electrometer] class is Coulomb's torsion-balance, which…
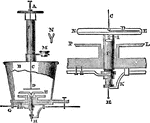
Dellman's Electrometer
"D is a needle, formed of light silver wire, suspended by a fine glass fiber, from a torsion head A.…

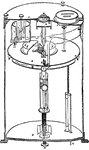
Disc Electrometer
"C is an insulated disc, over which is suspended another disc, hung from the arm of a balance, and connected…
Henleys Electrometer
"The electrometer of Henley, sometimes called Henley's quadrant Henley electrometer, may be taken as…
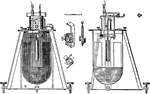
Quadrant Electrometer
"Elevation and section of Thomson's Quadrant Electrometer." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893
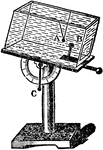
Sine Electrometer
"The sine electrometer of August, is a modification of the single pendulum electroscope, analogous in…