Clipart tagged: ‘Flagellate’
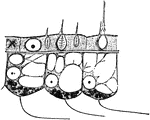
Body-wall
"Portion of the body-wall of Hydra, showing ectoderm cells above, separated by "structureless lamelia"…

Sponge Canal System
"Diagram showing types of canal system. --After Korschelt and Heider. The flagellate regions are dark…

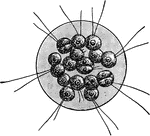
Cercomonad Flagellate
"A colony of Cercomonas termo, a typical flagellate infusorian." -Whitney, 1911
Euglena
Euglena viridis is a species of unicellular protists in the Euglenaceae family of flagellate organisms.

Flagellate Infusoria
Infusoria is an obsolete collective term for minute aquatic creatures like ciliates, euglenoids, protozoa,…
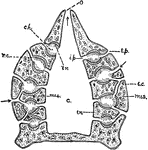
Sponge
"Diagram of simple type of sponge. c, cloaca; ch, chambers, lined with flagellate entoderm; e.p., external…
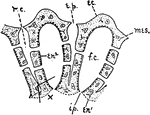
Sycon Sponge
Diagram showing the Sycon type of sponge. ec., ectoderm; r.c., radiating canals; i.p., internal pores;…