Clipart tagged: ‘flatworm’
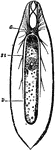
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…

Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
Flatworm
Flatworms are flattened, leaf-like forms living in damp places on land, in freshwater streams of ponds,…
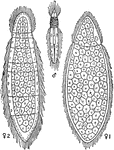
Rhopalura Gairdii Flat Worm
Illustration showing different rhompalura gairdii flat worms. The left and the right worms are the female,…
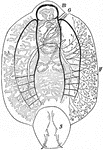
Microstomum
"Diagrammatic sagittal section of Microstomum, showing a chain of four zooids produced by fission. b,…
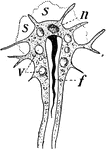
Nervous System of the Flatworm
Nervous system of a flatworm. Labels: G, cerebral ganglia and eyes; St, the two lateral nerve trunks;…
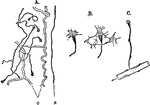
Protonephridium
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a flatworm. A, part of the excretory apparatus…
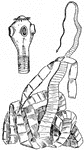
Tapeworm
The cestodes or tapeworms (Toenia solium), are parasitic flatworms. The body is usually of great length…
