Clipart tagged: ‘galvanometer’
Arc lamp
"In all the arc lamps in common use, the coil, by means of which the automatic maintenance of the arc…
Astatic Multiplier
"The coil is of flat, rectangular shape, with a narrow central opening just large enough to allow one…
Wheatstone Bridge
A device used to measure an unknown resistance of a resistor by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit.
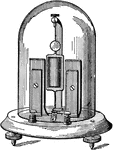
Deprez-d'Arsonval Dead-Beat Reflecting Galvanometer
"In the Deprez-d'Arsonval dead-beat galvanometer, a moveable coil is suspended between the poles of…
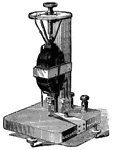
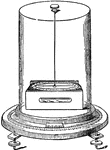
Electrodynamometer
"An electrodynamometer is a galvanometer with two coils, at least one of which is movable, and through…

Funnel-shaped Brass
A funnel-shaped piece of brass is placed over the ends of a galvanometer when the resistance is equal…
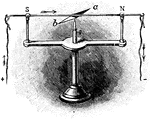
Galvanometer
A galvanometer is a type of ammeter; an instrument for detecting and measuring electric current. It…

Astatic galvanometer
"The galvanometer is an instrument for determining the strength of an electric current by means of the…

Tangent galvanometer
"The galvanometer is an instrument for determining the strength of an electric current by means of the…
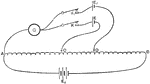
Potentiometer
A potentiometer instrument for measuring the potential (or voltage) in a circuit taps off a fraction…
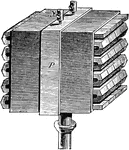
Thermomultiplier
An illustration of Macedonio Melloni's thermomultiplier, a combination of thermopile and galvanometer.
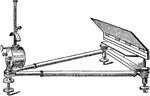
Thomsons Galvonometer
"A very convenient form of Thomson's galvanometer, the only specimen of its kind we have seen. The peculiarity…
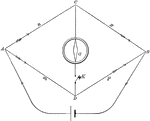
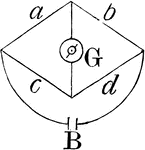
Wheatstone Bridge
"The Wheatstone bridge is used as a way to measure resistance of a unknown resitors." -Avery 1895
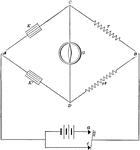
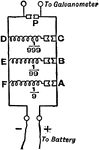
Wheatstone Bridge in Circuit
"The Wheatstone bridge is used as a way to measure resistance of a unknown resitors." -Avery 1895
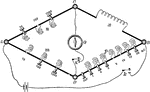
Wheatstone Bridge with Resistors
"The Wheatstone bridge is used as a way to measure resistance of a unknown resitors." -Avery 1895
