Clipart tagged: ‘ganglion’
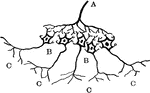
Diagram of the Relation between Cerebrospinal and Sympathetic Neurons
Diagram showing the relation of the cerebrospinal to the sympathetic neurons. Labels: A, a medullated…
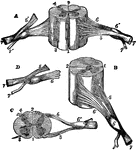
Sections of Cervical Spinal Cord
Views of section of cervical cord. Labels: A, anterior surface; B, right side; C, upper surface; D,…
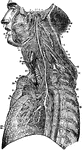
The Ninths, Tenth, and Eleventh Cranial Nerves
The ninth, tenth, and eleventh cranial nerves. Labels: 1, Gasserian ganglion; 2, internal carotid; 3,…
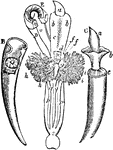
Dentalium
"Dentalium: B, the shell of Dentalium Entalis, broken longitudinally, showing the animal in a contracted…
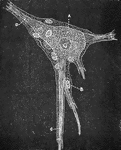
Ganglion Cell, Structure of
An isolated ganglion cell of a human, showing sheath with nucleated cell lining, B. A Ganglion cell,…
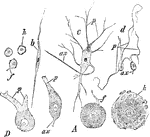
Different Forms of Ganglion Cells
Different forms of ganglion cells. A, a, round ball-shaped unipolar cell from the human Gasserian ganglion.…
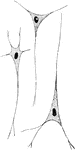
Ganglion Nerve Corpuscles
Nerve cells, also known as nerve corpuscles, comprise the second principle element of the nervous tissue.…
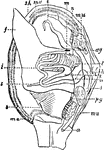
Mollusc Anatomy
"Anatomy of an Acephalous Mollusc (Mactra): s, stomach; ii, intestine; ag, anterior ganglions; pg, posterior…
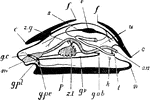
Mollusc Parts
"Ideal mollusc. m., Mouth; g.c., cerebral ganglia; c., edges of mantle skirt; z.g., duct of right lobe…
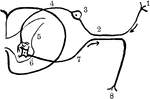
Nerve Reflex Arc
Reflex arc, as it is approximately in man. Labels: 1, nerve terminal, or sensory epithelium; 2, dendrite…
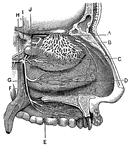
Nerves of the Nostril
"A, branches of the nerves of smell; B, nerves of touch to the nostrils; E, F,…

Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Base of Brain
Base of brain, spinal cord, and spinal nerves. Labels: V, 5th nerve; VI, 6th nerve; VII, a, facial nerve,…
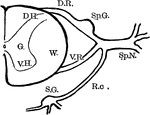
Spinal Nerve Roots
Diagram showing anatomy of the spinal nerve roots and adjacent parts. Labels: G., gray matter of the…
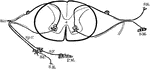
Spinal Nerve Roots
Diagram showing relation of neurons composing the spinal nerve roots with adjacent nervous structures.…
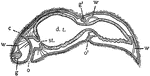
Stenostoma
In this Turbellarian the digestive tract (d.t.) is a blind sac. st., boundary of stomodaeum and mesenteron;…
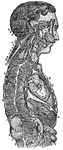
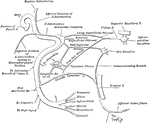
The Sympathetic Ganglions and their Connection to other Nerves
The sympathetic ganglions and their connection with other nerves. Labels: A, The semilunar ganglion…
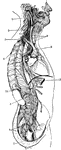
General View of the Sympathetic Nervous System
General view of the sympathetic nervous. Labels: 1,2,3, cervical ganglia; 4, 1st thoracic ganglion;…
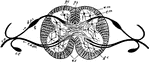
Vertebrate Spinal Cord
"Diagrammatic section of spinal cord. p.f., Posterior fissure; p.c., posterior column of white matter;…