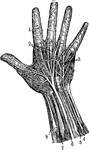
Hand
1. Nerves of the skin 2. Tendons 3. Arteries of the palm of the hand 4. Elbow nerve 5. Elbow artery…

Hands Shaking & Man at Attention
An illustration of two hands shaking with a man standing in the distance at attention.
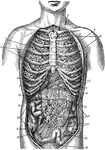
Internal Anatomy
1. Collar bone 2. Left Lung 3. Breast Bone 4. Right Lung 5. Ribs 6. Right lobe of the liver 7. Left…
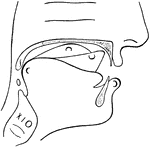
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols for Consonants
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols - Consonants. In representing the consonant a peculiar…
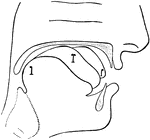
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols for Vowels
Physiological Bases of the Visible Speech Symbols - Vowels. In representing the vowel classification…

Pocketwatch
Gulliver shows the Lilliputians his gold pocketwatch. Never seeing anything like it before they believed…

The Eye of the Master Does More Work than Both His Hands
"The workmen all their master will obey, / They plane and saw, and dare not stop to play; / Each boy…
Upper Extremity
The upper extremity of the human body. 1: Clavicle; 2: Scapula; 3: Humerus; 4: Ulna; 5: Radius; 6: Carpus;…
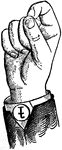
Round Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
Round Front Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Round Front Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
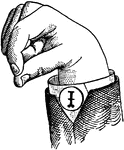
Round Mixed Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
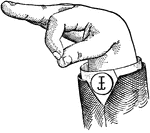
Round Mixed Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…

Normal Aperture Back Primary Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
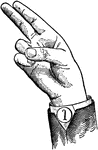
Normal Aperture Back Wide High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
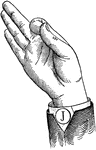
Normal Aperture Back Wide Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
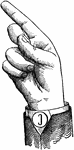
Normal Aperture Back Wide Mid Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
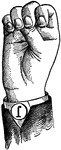
Normal Aperture Front Primary High Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…
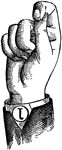
Normal Aperture Front Primary Low Vowel
Vowels have a wide, firm, and free channel, whereby the breath is modified without friction or sibilation.…