Clipart tagged: ‘nucleus’
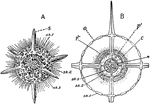
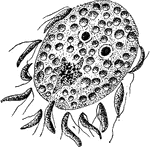
Actinomma
"Actinomma, a radiolarian with a shell and no mouth. A, whole animal with a portion of two spheres of…
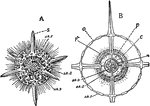
Actinomma Asteracanthion
"Actinomma Asteracanthion, a Radiolarian with a limited number of specialized radii (axes), symmetrically…
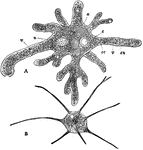
Amaeba Proteus
"Amaeba proteus; B, Amaeba radiosa. n, nucleus. c, contractile vacuole. a, food engulfed. ec, one of…
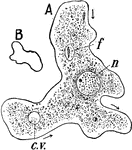
Amoeba
Amoung the simplest one-celled animals living in the ooze at the bottom of nearly every freshwater stream…
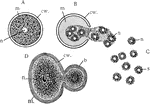
Amoeba Cell Division
"Direct cell division (Amoeba). A, active specimen with pseudopodia; B, becoming spherical preliminary…
Cell
"In a general what we may describe a cell as a tiny mass of jelly in which floats another still smaller…
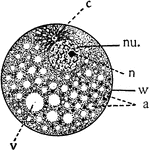
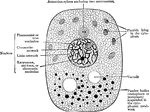
Cell
Diagram showing the principal parts of the cell and something of the protoplasmic architecture as it…
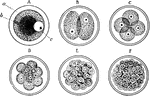
Cell Development
Every human body begin as a single nucleated cell. This cell, known as the ovum, divides or segments…

Cell Division
Diagram showing the change which occur in the centrosomes and nucleus of a cell n the process of mitotic…
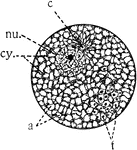
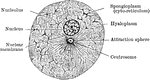
Cell Parts
"Diagram showing the principal parts of the cell as it appeaers when killed and stained. The protoplasm…
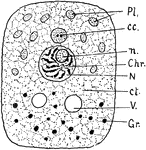
Cell Structure
"Diagram of cell structure. Pl. Plastids in cytoplasm. cc. Centrosome. n. Nucleolus. Chr. Chromosomes.…
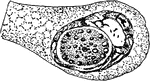
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Egg-cell
An illustration of the formation of the Cyclospora Cayetanensis egg-cell.
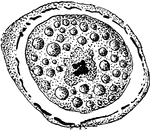
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Egg-cell
An illustration of the formation of the Cyclospora Cayetanensis egg-cell.
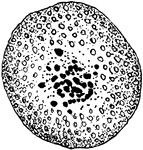
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Egg-cell
An illustration of the formation of the Cyclospora Cayetanensis egg-cell.
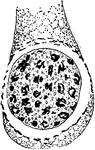
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Spermatozooids
An illustration of the formation of the CCyclospora Cayetanensis spermatozooids
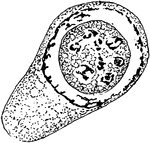
Growth of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Spore in Nucleus
An illustration of the growth of a Cyclospora Cayetanensis Spore in the nucleus.
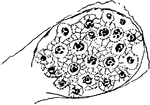
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Spores
An illustration of the growth of spores of a Cyclospora Cayetanensis.
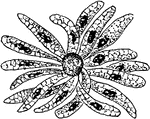
Formation of Cyclospora Cayetanensis Spores
An illustration of the growth of spores of a Cyclospora Cayetanensis.
Fertilization of Cyclospora Cayetanensis
An illustration of the fertilization of the egg by the spermatozooids of a Cyclospora Cayetanensis.

Fusion of Egg and Sperm-nuclei of Cyclospora Cayetanensis
An illustration of the fusion of egg and sperm-nuclei of a Cyclospora Cayetanensis.
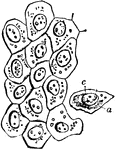
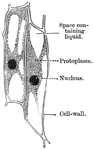
Flat Epithelium Cells
Flat epithelium cells from the surface of the peritoneum. Labels: a, cell body; c, nucleus.
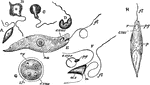
Euglena Viridis
"Euglena viridis. A-D, four views illustrating euglenoid movements; E and H, enlarged views; F, anterior…
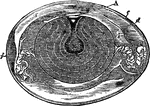
Hen's Egg
" Fig 110 - Hens egg, nat. size, in section; from Owen, after A. Thompson. A, cicatricle or "tread,"…
Human Spermatozoa
"One of the numberless microscopic bodies contained in semen, to which the seminal fluid owes its vitality,…
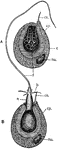
Hydra
"Nettling cells of Hydra. A, unexploded; B, exploded; b, barbs; c, the nettling cell in which the nettling…
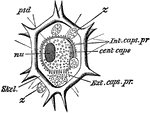
L. Annularis
"Liteocircus annularis. cent. caps, central capsule; ext. caps. pr, extra-capsular protoplasm; int.…
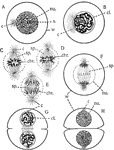
Mitotic Division
"Indirect or mitotic division; A, resting mother nucleus; B, coil stage, with the centrosomes separating;…
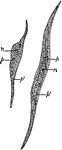
Muscle Fibres
"Plain muscle fibres. n, nucleus of muscle cell; p, undifferentiated cell protoplasm; p', the differentiated…
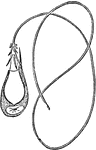
Nematocyst
"Nematocyst of Hydra, showing cell-substance and nucleus, cyat, trigger hair, and everted thread." —…
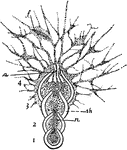
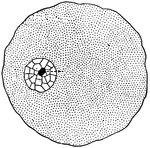
Nodosaria
"A compound foraminiferan, Nodosaria. a, aperture of shell; f, food particles captured by the strands…
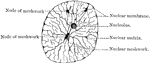
Nucleus at Rest
The nucleus when in a condition of rest is bounded by a distinct membrane, possibly derived from the…
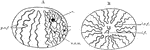
Nucleus Showing Chromatic Filaments
Diagrams of the nucleus showing the arrangement of chief chromatic filaments. A, Viewed from the side,…
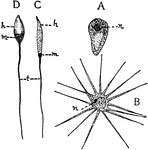
Spermatozoa
"Types of spermatozoa. A, from the round worm (Ascaris) with a cap, somewhat amaeboid; B, from the Crayfish,…
Spermatozoa of an Ape
"One of the numberless microscopic bodies contained in semen, to which the seminal fluid owes its vitality,…
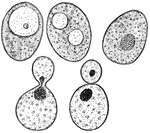
Yeast cake
"Showing a Bit of Common Yeast Cake when mixed with Water and examined under the Microscope. There are…