Clipart tagged: ‘sphenoid’
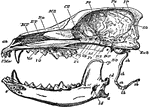
Dog Skull
"Longitudinal and Vertical section of the skull of a dog, with mandible and hyoid arch. an, anterior…
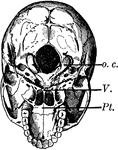
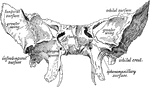
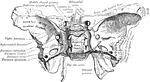
Base of the Skull
The base of the skull. The lower jaw has been removed. At the lower part of the figure is the hard palate…
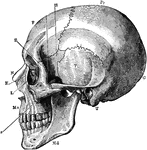
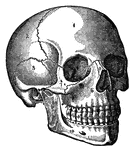
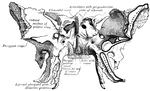
Side View of the Skull
A side view of the skull. Labels: O, occipital bone; T, temporal; Pr, parietal; F, frontal; S, sphenoid;…
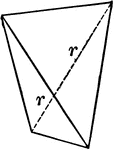
Sphenoid
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
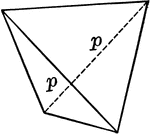
Sphenoid
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
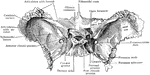
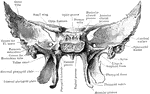
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
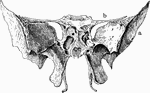
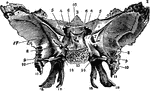
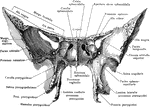
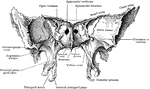
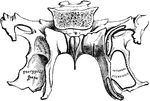
Sphenoid Bone of the Human Skull
Sphenoid bone, situated the anterior part of the base of the skull, articulating with all the other…
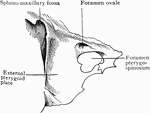
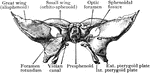
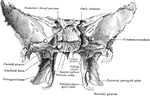
Sphenoid Bone Showing Foramen Pterygospinosum
Portion of sphenoid bone, showing the foramen pterygospinosum.
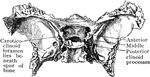
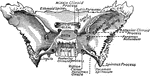
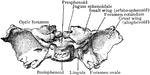
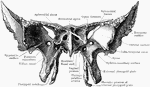
Abnormal Sphenoid Bone
Sphenoid bone, showing abnormal development of middle clinoid processes, especially on the left side.
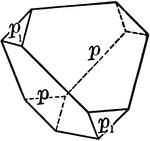
Sphenoid, positive and negative
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
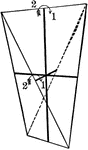
Symmetry of Sphenoidal class
"The Sphenoidal Class corresponds in the Tetragonal system to the Tetrahedral class in the Isometric…