This ClipArt gallery offers 142 illustrations of the anatomy of fish, including organ diagrams, skeletal diagrams, fish eggs, and more for numerous species.
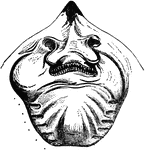
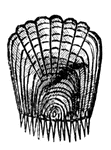
Californian Hagfish
"Bdellostoma stouti (Californian hag), enveloped in sheath of mucus. b., barbules e., eyes m. mucus;…
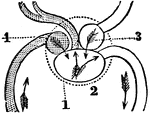
A Diagram of the Heart of a Fish
A diagram of the heart of a fish. Labels: 1, Pericardium. 2, The ventricle that receives the blood from…
Hyoid Arch
"Hyoid arch, branchial apparatus, and scapulary arch of the Perca." — Encyclopedia Britannica,…
Lamellae
"Diagram to show the way in which an outgrowing gill-process bearing blood-holding lamellae, may give…
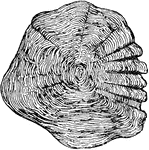
Queensland Lungfish Fin
"Skeleton of Ceratodus fin. a., Central axis; r., radials; h., basal piece." -Thomson, 1916
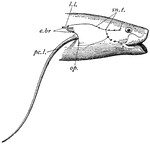
African Lungfish Head
"Head region of Protopterus. sn.t., Sensory tubes; l.l., lateral line; e.br., external gills; pc.l.,…
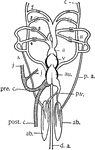
African Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of the heart and branchial arches in Protopterus (one of the Dipno). pre.c., precaval vein,…
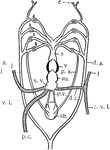
Queensland Lungfish Heart
"Diagram of heart and branchial arches in Ceratodus (one of the Dipnoi). a.b., air bladder (lung); p.a.,…
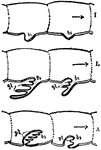
Metamorphosis of a Flounder
Flounder have both eyes situated on one side of the head, they are not born this way. Their life involves…
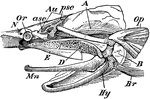
The Skull of a Paddle-Fish with the Beak Removed
"Skull of Spatularia, with the long beak removed, the anterior (asc) and posterior (psc) semicircular…
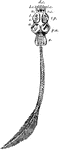
Palaeospondylus Gunni
"Restored skeleton of Palaeospondylus gunni. d.c., Cirri of dorsal margin; l.c., long lateral cirri;…
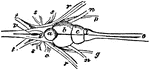
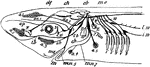
Perch Brain
"Brain of Perch. Upper aspect. a, cereoellum; b, optic lobes; c, hemispheres; e, lobi inferiores; f,…
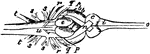
Perch Brain
"Brain of Perch. Lower aspect. a, cereoellum; b, optic lobes; c, hemispheres; e, lobi inferiores; f,…
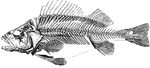
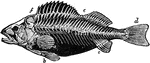
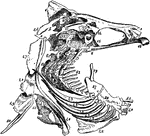
Perch skeleton
"The bones of fishes are of a less dense and compact nature than in the higher order of animals; in…
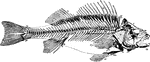
Perch Skeleton
"The spinal column consists of abdominal and caudal vertebre, the coalescence of the parapophyses into…
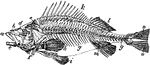
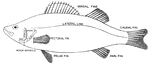
Skeleton of Perch
"Skeleton of Fish (Perch). a, intermaxillaries; b, nasal region; c, dentary bone of mandible; d, orbit…
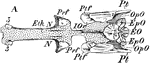
Pike Cranium
"Cartilaginous Cranium of the Pike (Esox lucius), with its intrinsic ossifications. A, top view; 3,…
Pike Cranium
"Cartilaginous Cranium of the Pike (Esox lucius), with its intrinsic ossifications. B, side view: V,…
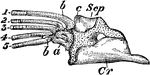
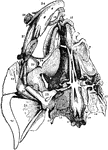
Pike Scapulocoracoid
"Pectoral arch and fore limb of the pike (Esox lucius), an osseous fish, showing scapulocoracoid, composed…
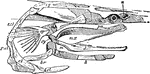
Polyodon
"Skull of Polyodon. n, nasal cavity; sq, squamosal; mh, hyomandibular; sy, symplectic; pa, palate-pterygold;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Upper aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lateral aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…
Polypterus Brain
"Brain of Polypterus. Lower aspect. a, medulia; b, corpora restiformia; c, cerebellum; d, lobi optici;…

Polypterus Skull
"Upper aspect of the primordial cranium, with the membrane-bones removed. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…
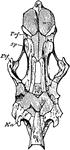
Polypterus Skull
"Lower aspect of the primordial cranium, with the membrane-bones removed. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…
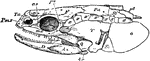
Polypterus Skull
"Side view, with the membrane-bones. An, angular; ao, anteorbital; Ar, articulary; B, basal; D, dentary;…
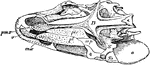
Polypterus Skull
"Lower aspect of the skull, part of the bones being removed on the side. An, angular; ao, anteorbital;…

Protonephridium of a Shark
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a shark. Labels: Wtr, ciliated funnels; Ug, segmental…
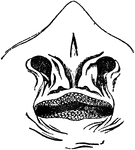
Raia Lemprieri
"Nostrils of Raia lemprieri, with nasal flaps reverted." — Encyclopedia Britannica, 1893
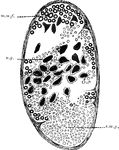
Ramus Viseralis
Transverse section of the ramus visceralis of the vagus of skate. Labels: v.g., visceralis ganglion;…

Roach Scale Arrangement
"Arrangement of scales in the Roach (Leuciscus rutilus). L, Lateral line; t r, transverse line; a, transverse…
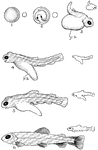
Salmon Development
"The early development of the salmon. 1, The fertilised egg; 2, the egg just before hatching; 3, the…

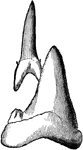
Sawfish Head
"The Sawfish is so called from the saw-like weapon into which the snout is produced. They are common…

Placoid Scale of Ray
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…

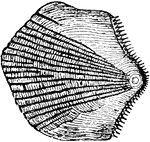
Ctenoid, Scale
Fishes are sometimes classed, in accordance with the structure of their scale, into Ctenoid, Ganoid,…
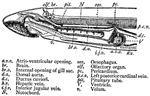
Cross Section View of a Sea Lamprey
An illustration of the median longitudinal section through anterior end of the sea lamprey. "a.v.o,…
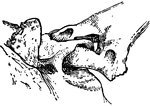
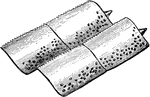
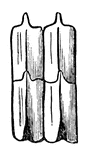
Shackle Joint from the Exoskeleton of a Siluroid Fish
"A joint involving the principle of the shackle. Specifically, in anatomy, a kind of articulation found…
!["Shark is an English popular name for any individual of the group Selachoidei. Sharks are scaleless, and the skin usually rough. They are numerous in tropical seas, becoming scarcer as they recede from the warmer regions, a few only reaching the Arctic circle. They are rapid swimmers, with great power of endurance; the larger sharks are exclusively carnivorous, and some of them extremely dangerous to man. They scent their food from a distance, and are readily attracted by the smell of blood or decomposing bodies. The flesh of sharks is coarse, but it is sometimes eaten. Their rough skin is employed by joiners to polish fine-grained wood, and by cutlers to cover the hilts of swords to make them firmer in the grasp. [Pictured] Egg of Scyllium Chilense"—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/16100/16199/sharkegg_16199_mth.gif)
Shark Egg
"Shark is an English popular name for any individual of the group Selachoidei. Sharks are scaleless,…
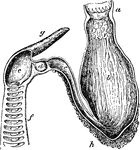
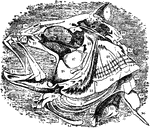
Shark Stomach
"Siphonal stomach and spiral valve of Basking-shark (Selache). a, esophagus; b, cardiac portion of stomach;…
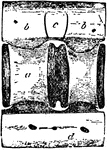
Shark Vertebra
"Lateral view of caudal vertebra of Basking Shark (Selache mazima). a, centrum; b, neurapophysis; c,…
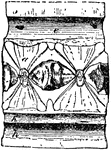
Shark Vertebra
"Longitudinal section of caudal vertebra of Basking Shark (Selache mazima). a, centrum; b, neurapophysis;…

Shark Vertebra
"Transverse section of caudal vertebra of Basking Shark (Selache mazima). a, centrum; b, neurapophysis;…