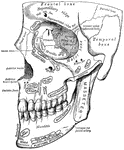
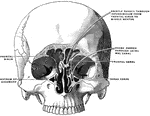
Clipart tagged: ‘cerebrum’
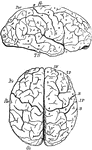
Brain
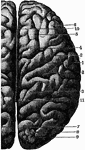
"Profile and vertex views of cerebrum. Dr, the frontal lobe; Par, parietal; Oc, occipital; Ts, temporo-sphenoidal…
Brain and Spinal Cord
Anterior view of the brain and spinal marrow. Labels: 1, 1, hemispheres of the cerebrum; 2, great middle…
Brain and Spinal Cord
The brain and spinal cord. Labels: 1, 1, hemispheres of cerebrum; 2, great middle fissure; 3, cerebellum;…
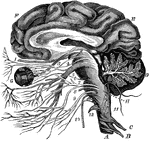
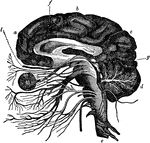
The Brain and the Cranial Nerves
The brain and the origin of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves. Labels: F, E, the cerebrum; D, the cerebellum,…
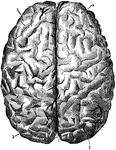
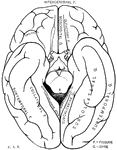
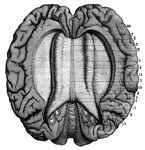
Brain Seen from Above
Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure separating the hemispheres; 2, frontal lobes of the cerebrum; 3, posterior…
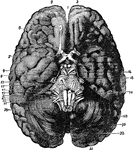
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure; 2, 2, anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3, olfactory…
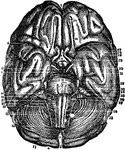
Base of the Brain
Base of the Brain. Labels: 1,2, longitudinal fissure; 3, anterior lobes cerebrum; 4, middle lobe; 5,…
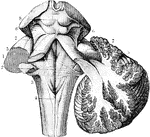
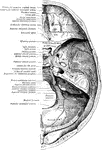
The Cerebrum and Fourth Ventricle of the Brain
The cerebellum in section and fourth ventricle, with the neighboring parts. Labels: 1, median groove…
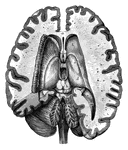
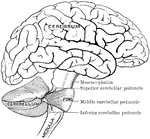
Human Brain
A top view of a dissection of the human brain showing the lateral fourth and fifth ventricles.
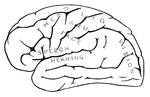
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which parts of the brain control hearing, speech, vision, legs,…
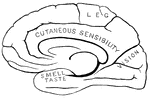
Human Brain
Side diagram of the human brain showing which areas perform the sense of taste, smell, and vision.
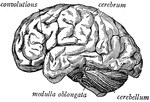
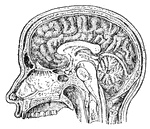
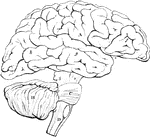
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
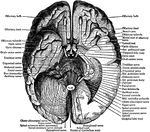
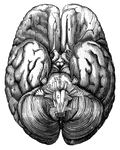
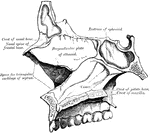
Under Surface of the Brain
View of the under surface of the brain, with the lower portion of the temporal and occipital lobes,…
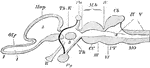
Vertical Section of a Vertebrate Brain
Longitudinal and vertical diagrammatic section of a vertebrate brain. Mb, midbrain: what lies in front…
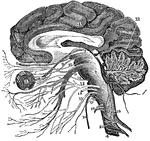
Vertical Section of the Brain
A vertical section of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata, showing the relation of the…
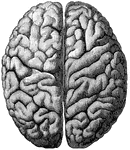
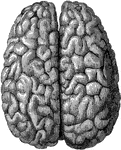
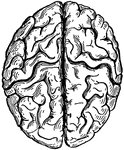
Cerebrum
"The Upper Surface of the Cerebrum. Showing its division into two hemispheres, and also of the convolutions."…
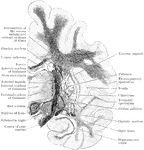
Coronal Section Through Cerebrum
Coronal section through the cerebrum of an orangoutang passing through the subthalamic tegmental region.
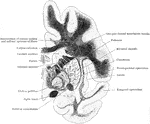
Coronal Section Through the Cerebrum
Coronal section through the left side of the cerebrum of an orangoutang. The section passes through…
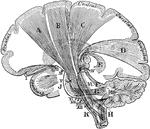
Projection Fibers of the Cerebrum
Diagram of the projection fibers of the cerebrum. Labels: B, motor (pyramidal) tract; C, body-sense…
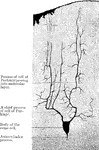
Cortical Gray Matter of the Cerebrum
The five layers of the cortical gray matter of the cerebrum. 1, Superficial layer with abundance of…
Outline of the Encephalon
Plan in outline of the encephalon, as seen from the right side. The parts are represented as separated…
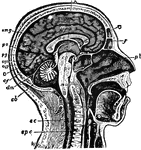
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…
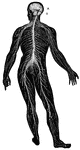
Nervous System
The human nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves. Labels: A, cerebrum; B, cerebellum.
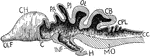
Vertebrate Brain
"Partial section of a Vertebrate brain (diagrammatic). OLF., Olfactory lobe; CH., cerebral hemispheres;…