Abacus
"In architecture the slab or plinth which forms the upper member of the capital of a column or pillar,…
Roman Aqueduct
"Part of a Roman Aqueduct. Aqueducts form one of the most characteristic features of Roman architecture.…

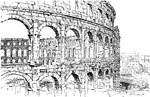
Roman Arcade with Engaged Columns
An arcade is a passage or walkway covered over by a succession of arches or vaults supported by columns.…

Arch of Constantine
The Arch of Constantine is a triumphal arch in Rome between the Colosseum and the Palatine Hill.
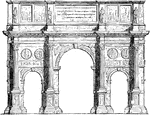
Arch of Constantine
"Triumphal arches from a class apart among the monuments of Roman architecture. It was an early custom…

Roman Astragal
"Roman Ovolo Molding, with Pearl Beading. The ornamentation had to correspond with the massive character…

Roman Astragal
"Ornamented Roman Astragal. The ornamentation had to correspond with the massive character of Roman…
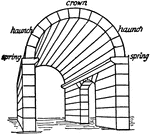
Barrel Vault
A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault or a wagon vault, is an architectural element formed by…

Tomb of Cæcilia Metella
"The usual form of independent monumental tombs was a ponderous tower-shaped block, sometimes square,…

Ruins of the Baths of Caracalla
The ruins of the baths of Caracalla were roman public baths built in Rome, Italy between AD 212 and…

The Cloaca Maxima at Rome
In these Etruscan buildings traces are to be found of the arch; as, for instance, in the Gate of Volterra…
Architecture of the Colosseum
The construction of arches and vaults did not remain confined to the interior of buildings, but imparted…
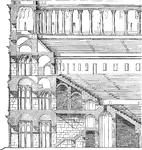
Elevation and Section of the Colosseum
"Elevation and Section of the Tiers of Seats and Substructure of the same from the Colosseum at Rome.…
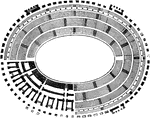
Ground Plan of the Colosseum
"Ground Plan of the Colosseum at Rome, with representation of the Tiers of Seats, and of the Substructure.…

Roman Colosseum
This Roman Colosseum is located in Rome, Italy. It is the largest elliptical amphitheater that was built…

Trajan's Column
The Trajan's column is a monument in honor of Emperor Trajan located in Rome, Italy. The column is a…

Semi-Columns
"Semi-columns (Roman). Engaged columns of the Maison Carrée, Nîmes, France." -Whitney,…

Roman Cornice
"Ornamented Cornice with Pearl Beading. The ornamentation had to correspond with the massive character…

Roman Cornice
"Richly Ornamented Roman Ovolo. The ornamentation had to correspond with the massive character of Roman…

Entrance Façade of Diocletian's Palace
"Fragment of the Entrance-Façade of the Palace of Diocletian at Spalatro. The tendency of the…
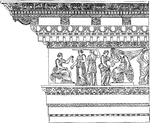
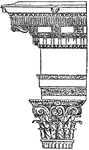
Corinthian Entablature from the Nerva at Rome
Simple styles, such as the Doric, which accorded so intimately with the whole disposition of the Grecian…
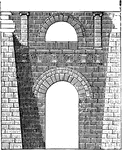
Etruscan Arch at Perugia
In these Etruscan buildings traces are to be found of the arch; as, for instance, in the Gate of Volterra…

Etruscan Tomb at Castel d'Asso
The most interesting monuments of Etruscan architecture which have been preserved are the tombs. They…
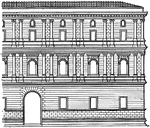
Façade of the Giraud Palace, Rome
In the Giraud Palace and the great Palazzo della Cancelleria, pilasters appear in the external composition,…

Fenestella in the Church of Norrey
"Fenestella. In Roman Catholic churches, a niche on the south side of an altar, containing the piscina,…
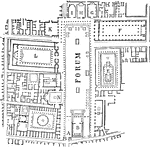
Forum of Pompeii
"Forum of Pompeii. A, principal entrance; B, a Corinthian temple; C, the public prison (carcer publicus);…

Ancient Roman Frieze
"Fragment of an Ancient Roman Frieze. The ornamentation had to correspond with the massive character…

Pont du Gard
The Pont du Gard is an aqueduct and bridge that was built over the Gard River by the Roman Empire. It…
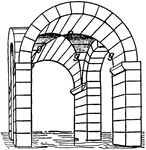
Groin Vault
A groin vault or groined vault (also sometimes known as a double barrel vault or cross vault) is produced…
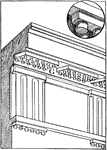
Gutta in Doric Architecture
"Guttae in Doric Architecture. A, form of gutta beneath regula; G, G, guttae beneath mutules and regulae.…
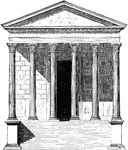
Maison Carrée
The Maison Carrée at Nîmes in southern France is one of the best preserved temples to be…
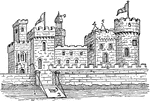
Medieval Castle
Medieval Castle of the Holy Roman Empire. "1 Moat, 2 Drawbridge, 3 Wicket, 4 Merlons, 5 Embrasures,…

Tomb of Nævoleia Tyche at Pompeii
"For tombs of smaller dimensions various forms and abnormal decorations were employed. An ornamented…

The Arena of Nîmes
The arena of Nîmes is a Roman amphitheater located in city of Nimes, France. The amphitheater was built…

The Square House of Nîmes
The square house of Nîmes is also known as Maison Carree. It is an ancient Roman temple located in…
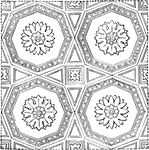
Ornament of a Vaulted Roof
Roman arches were, as a rule, ornamented with sunken panels of various shapes, in which were introduced…

Ornament of a Vaulted Roof
Roman arches were, as a rule, ornamented with sunken panels of various shapes, in which were introduced…
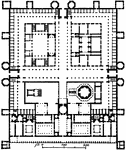
Palace of Diocletian, Plan
Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palaca in Croatian) is a building in Split in Croatia that was built…

Façade of the Pantheon at Rome
"The most important and most beautiful of circular buildings without columns surrounding it is the Pantheon…

Interior of the Pantheon at Rome
"The most important and most beautiful of circular buildings without columns surrounding it is the Pantheon…

Street of Tombs at Pompeii
"For tombs of smaller dimensions various forms and abnormal decorations were employed. An ornamented…

The Pantheon at Rome
The pantheon at Rome is a temple that was built to all the gods of Ancient Rome. It was built by Marcus…
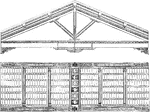
Profile of San Miniato al Monte
"Profile and view from beneath of the Rafters in the Christian Basilica of San Miniato at Florence.…
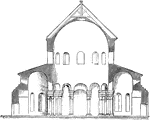
Santa Costanza
"Section of the Church of S. Constantia at Rome. The simplest desctiptions of this kind of building…
Tower of Santa Maria in Cosmedin
"Tower of the Early Christian Basilica of S. Maria in Cosmedin at Rome." Santa Maria in Cosmedin (or…