Clipart tagged: ‘starch’
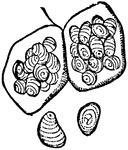
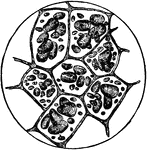
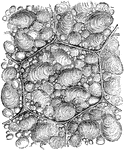
Starch Cells
"a, Starch cells of the Pea, showing grains of starch in the interior. b, Seperate starch grains, with…

The Lentil Plant
This illustration shows a lentil plant. Lentils are the round, flat seeds of a small leguminous plant…

Maize
A native of America, is extensively cultivated from the southern part of Chili to high latitudes in…
Carrot Root
Roots of the carrot are designed to absorb moisture and matter from soil, and to hold nutrients for…
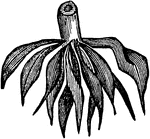
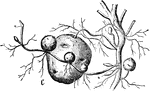
Fasciculated Root
"When the fibers of roots become enlarged by the deposition of starch, they form this variety of root."—Darby,…
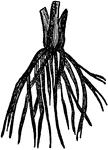
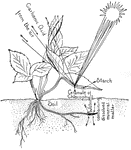
Fibrous Root
"This variety consists of numerous fibers proceeding from the neck of the plant, and may be seen in…

Turnip Root
Roots of the turnip are designed to absorb moisture and matter from soil, and to hold nutrients for…
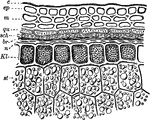
Wheat Grain
"Section through exterior part of a grain of wheat. c, cuticle or outer layer of bran; ep, epidermis;…

Yam
Yam is the common name for some species in the genus Dioscorea (family Dioscoreaceae).These are perennial…